-
CATEGORY ::
- All Seeds /
- All Cover Crop Seed
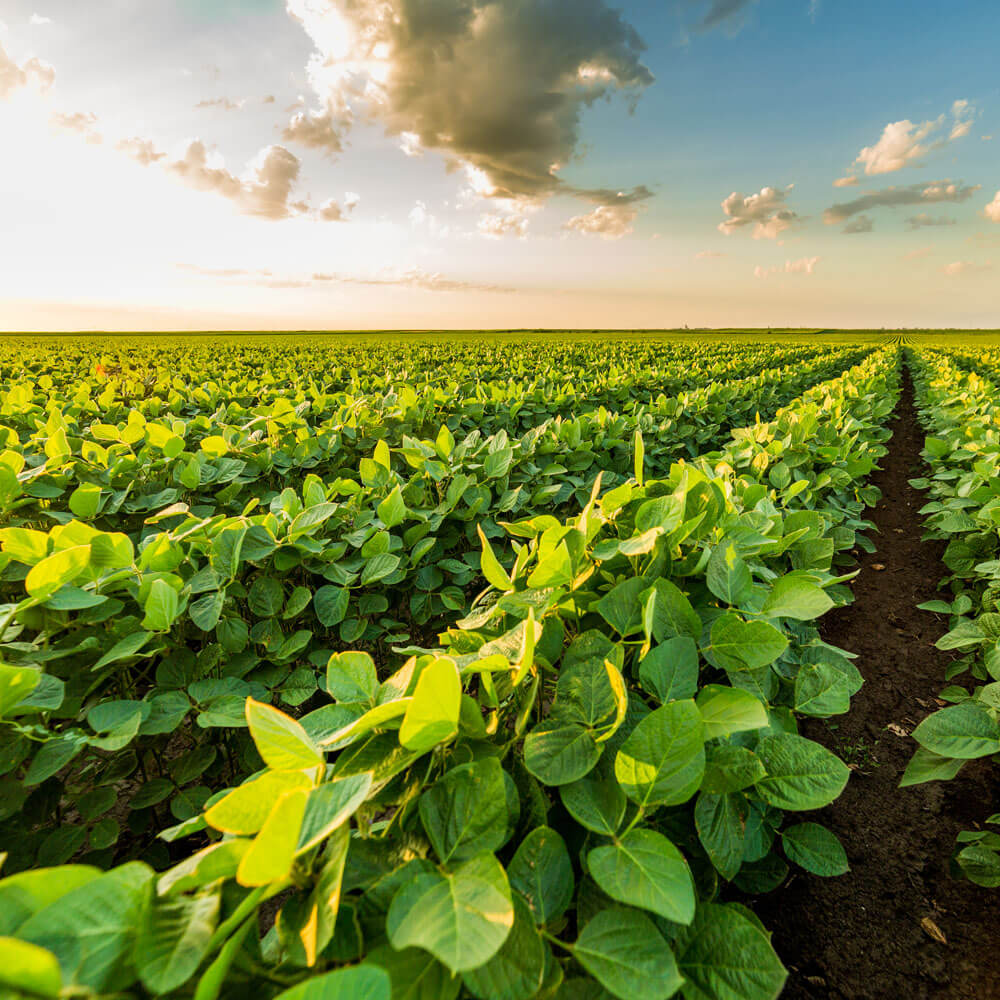
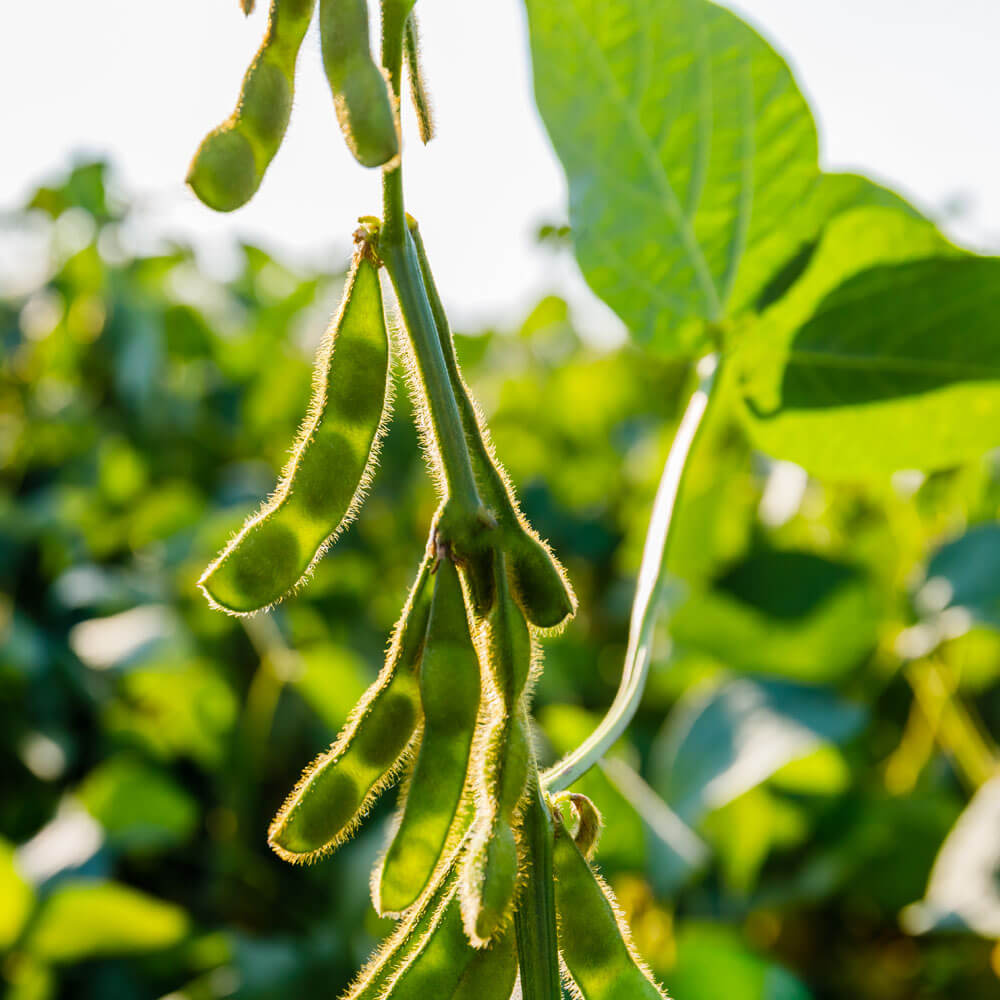
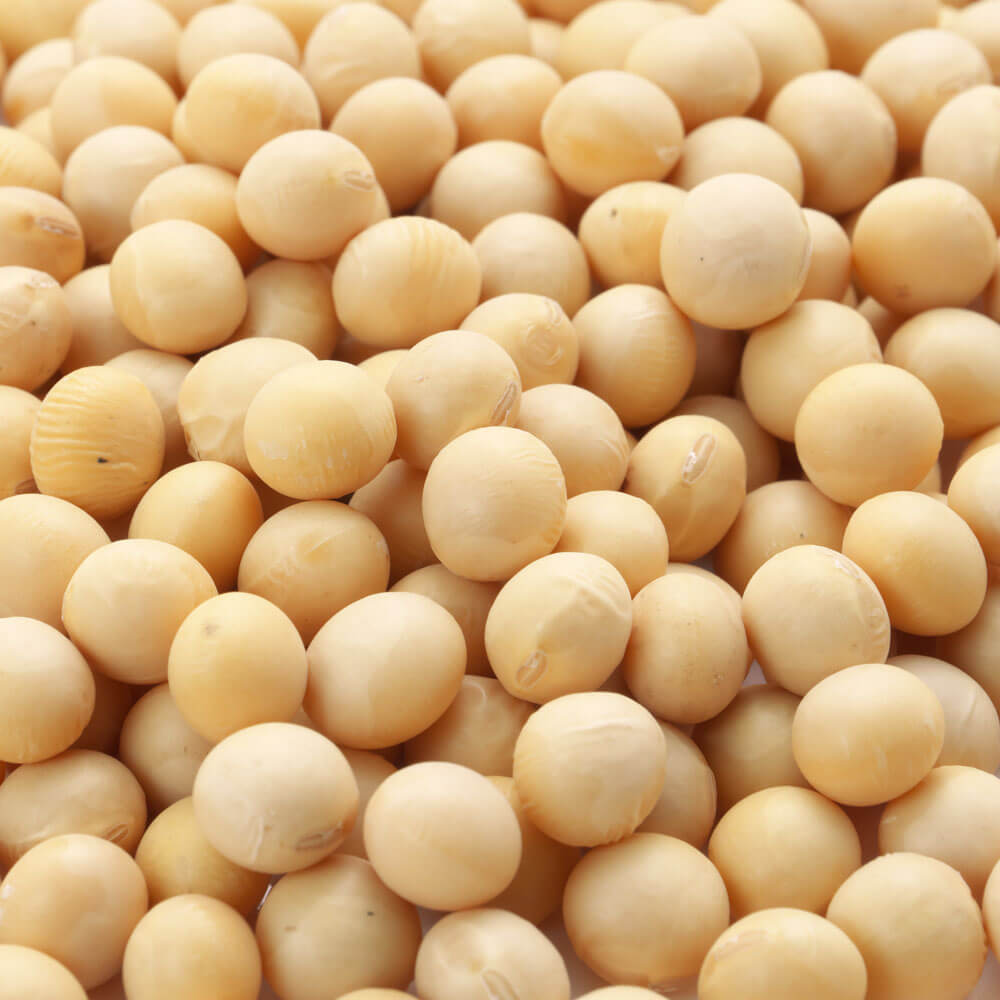










Soybean Seeds
LATIN NAME
Fagopyrum esculentum
SEASON
Annual
WHEN TO PLANT
Late spring to mid summer
MOISTURE REQUIREMENTS
Moderate
CROP HEIGHT
36 - 48 inches
COLD TOLERANCE
Excellent
HEAT TOLERANCE
Good
SHADE TOLERANCE
Poor
DAYS TO MATURITY
70 - 90 days
PLANT CHARACTERISTICS
Wear tolerant, fast growing, improves soil, nutritious grain
LATIN NAME
Brassica oleracea
SEASON
Annual
WHEN TO PLANT
5 - 7 weeks before frost in fall
MOISTURE REQUIREMENTS
Moderate
CROP HEIGHT
36 inches
COLD TOLERANCE
Excellent
HEAT TOLERANCE
Fair
SHADE TOLERANCE
Good
DAYS TO MATURITY
55 - 75 days
PLANT CHARACTERISTICS
Excellent regrowth, winter hardiness, erosion control
LATIN NAME
Trifolium incarnatum
SEASON
Annual
HEIGHT
12 - 18 inches
BLOOM COLOR
White
PLANT CHARACTERISTICS
Easy to establish, weed supression
MOISTURE REQUIREMENTS
Moderate
ACIDIC SOIL TOLERANCE
Moderate
COLD TOLERANCE
Good
HEAT TOLERANCE
Good
SHADE TOLERANCE
Good
FERTILITY NEEDS
Low
MATURE HEIGHT
12 - 18 inches
LATIN NAME
Vicia faba
SEASON
Annual
WHEN TO PLANT
After danger of frost
MOISTURE REQUIREMENTS
Moderate - high
CROP HEIGHT
48 inches
COLD TOLERANCE
Fair - good
HEAT TOLERANCE
Moderate
SHADE TOLERANCE
Fair - good
DAYS TO MATURITY
80 - 100 days
PLANT CHARACTERISTICS
Nitrogen fixator, high yields, high protein, high biomass
About...
Soybeans (KS 5120N) - An heirloom variety which features good resistance to soybeans cyst nematode and soybean mosaic virus. It is an annual legume of the pea family which has edible seeds. The soybean is economically the most important bean in the world, providing vegetable protein for millions of people and ingredients for hundreds of chemical products.



MORE COVER CROP OPTIONS
Planting Directions
SOWING TEMPERATURE
55F - 77F
SEEDING RATE
90 - 120 lbs per acre
AVERAGE GERMINATION TIME
5 - 10 days
PLANTING DEPTH
3/4 - 1 1/2 inches
SOWING METHOD
Broadcast or drill
ENVIRONMENT
Full sun
USDA ZONES
2 - 10
ESTABLISHMENT RATE
Fast









Soybeans (KS 5120N) - An heirloom variety which features good resistance to soybeans cyst nematode and soybean mosaic virus. It is an annual legume of the pea family which has edible seeds. The soybean is economically the most important bean in the world, providing vegetable protein for millions of people and ingredients for hundreds of chemical products.
When the farmer sells soybeans to a grain dealer, the beans may then go to a number of ultimate destinations. When processed, a 60-pound bushel will yield about 11 pounds of crude soybean oil and 47 pounds of soybean meal. Soybeans are about 18% oil and 38% protein. Because soybeans are high in protein, they are a major ingredient in livestock feed. Soybeans are processed for their oil and meal. A smaller percentage is processed for human consumption and made into products including soy milk, soy flour, soy protein, tofu and many retail food products. Soybeans are also used in many non-food industrial products.
Soybean processors bake the high-protein fiber that is left after the oil is removed and sell it for animal feed. Soybean oil is used in cooking and frying foods. Margarine is a product made from soybean oil. Salad dressings and mayonnaises are made with soybean oil. Some foods are packed in soybean oil such as: tuna and sardines. Baked breads, crackers, cakes, cookies and pies usually have soybean oil in them.
The high-protein fiber which remains after processing has removed the oil is toasted and prepared into animal feed for poultry, pork, cattle, other farm animals and pets. The poultry and swine industries are major consumers of soybean meal. Over half of the soybeans processed for livestock feed are fed to poultry, about one-quarter is fed to swine, and the rest is used for beef cattle, dairy cattle and pet food.
Planting Directions
SOWING TEMPERATURE
50F - 70F
SEEDING RATE
40 - 50 lbs per acre
AVERAGE GERMINATION TIME
3 - 5 days
PLANTING DEPTH
1/2 - 1 inch
SOWING METHOD
Broadcast or drill
ENVIRONMENT
Full sun
USDA ZONES
3 - 10
ESTABLISHMENT RATE
Fast





Reasons to grow buckwheat:
- Fits into rotations at a time when fields might otherwise be idle.
- Can be grown as a catch crop where another crop failed.
- Inexpensive to grow because it requires no pesticides and little fertilizer.
- Can be grown with equipment available on most farms.
- Requires little attention during the growing season.
- Mellows the soil and suppresses some weeds.
- Easily raised Organically, at a premium price.
For more information from Cornell University: Buckwheat
Planting Directions
SOWING TEMPERATURE
45F+
SEEDING RATE
10 - 15 lbs per acre
AVERAGE GERMINATION TIME
7 - 14 days
PLANTING DEPTH
1/2 inch
SOWING METHOD
Broadcast or drill
ENVIRONMENT
Full sun to partial shade
USDA ZONES
2 - 9
ESTABLISHMENT RATE
Fast









Purple Top Turnip (Brassica Rapa) - An easy to grow plant from purple top turnip seeds used for forage and cover crops. This turnip is white and purple that has smooth, globe roots take about 55 days to reach maturity. This plant has many great uses such as putting nutrients back into the soil as well as providing a food source for wildlife and livestock. They grow rapidly and are an excellent choice for fall grazing livestock and used widespread for deer food plots. This dual-purpose plant produces a large purple top spherical root and leafy foliage that can both be grazed. Because they provide a high-protein and high-energy food source, purple top turnips are one of the most popular food plot plants for whitetail deer as well as a general purpose cover crop.
Smaller size turnips remain sweet and tender and are therefore a desirable food source for deer. Cool temperatures also help enhance the taste of the turnip making them great for hunting season food plots that can be planted in mid to late summer and provide forage into the winter months. Deer will graze on the greens and leave the turnip underground untouched as a sort of food reserve and will return once the greens are gone and even after snow fall and will dig through the snow and dig up and eat the purple top turnip providing an important high energy winter food source. Turnips are an annual plant growing in USDA Zones 2 - 9 and usually reach a height of 24 inches.
Planting Directions
SOWING TEMPERATURE
45F+
SEEDING RATE
6 - 10 lbs per acre
AVERAGE GERMINATION TIME
3 - 14 days
PLANTING DEPTH
1/4 inch
SOWING METHOD
Broadcast or drill
ENVIRONMENT
Full sun
USDA ZONES
3 - 10
ESTABLISHMENT RATE
Fast









Bayou Kale (Brassica oleracea) - is a winter hardy member of the Brassica family that is highly digestible. It is known for its large, palatable leaves. and can provide up to 25% protein. High digestible forage for deer that is ideal for extended grazing in wildlife food plots providing quality winter forage. Kale has the highest cold tolerance of all the Brassicas, good winter hardiness and a high leaf to stem ratio. It may be grown both as a spring and early fall crop for winter grazing. Kale grows best in cooler weather with cold days and nights which will sweeten the leaves especially if subjected to a fall frost. Remember that Kale grows large leaves and may over shade other plants in your food plot. Kale prefers a pH of 5.5 to 7.0.
Bayou kale is a mid-maturing forage brassica with a smooth leaf, and a nutty flavor that is sweet to human taste. This kale variety has a smaller stem but can grow up to 3 feet tall. Bayou has excellent regrowth when rotationally grazed, and the stems are more palatable than forage rapes for cattle and sheep. Used in food plots for deer as well as upland game birds, animals will eat the Bayou first when planted beside other food plots.
When planted in late summer or early fall, it is considerably more winter-hardy than radishes and helps control erosion. The spring green-up of Bayou kale is similar to forage rapes, while its seed size and crop management are similar to other brassicas, like turnips. Seed should be planted at 6 - 10 lbs/ac when planted as a single specie and 2 - 3 lbs/ac when mixed with other crops. Recommended planting time for Northern Regions is summer when night time temperatures are consistently below 65 degrees. Planting should occur July - September for the Midwest and September - October for the South.
Forage Kale has show to help in opening up the soil because of its tap roots. As a cover crop kale can be planted in late summer or early fall; using it as a winter crop helps protect the soil longer from erosion.
Product Specifications:
- Excellent regrowth
- Forage brassica
- Good winter hardiness
- Great for food deer food plots
- Protects soil from erosion
- Use for: pasture, food plot, cattle forage, livestock grazing, cover crop
Planting Directions
SOWING TEMPERATURE
65F+
SEEDING RATE
25 - 50 lbs per acre
AVERAGE GERMINATION TIME
3 - 7 days
PLANTING DEPTH
1/4 - 1 inch
SOWING METHOD
Broadcast or drill
ENVIRONMENT
Full sun
USDA ZONES
8 - 11
ESTABLISHMENT RATE
Fast









Sunn hemp (Crotalaria juncea L.) - is a legume commonly used as a cover crop for southern and sub-tropical and tropical farming systems. It has recently been more adopted in the Midwestern United States cropping systems. Sunn hemp has high rates of biomass production — over 20 percent greater than crimson clover and hairy vetch in research trials. In as little as 60 to 90 days it can produce 120 pounds of nitrogen per acre and can suppress weeds up to 90 percent.
Sunn Hemp is adapted to a wide variety of soil and environmental conditions, thriving through hot, dry summers and continuing to grow until the first frost. But sunn hemp isn’t just a soil builder — it also offers benefits as a forage producer. Sunn hemp is easy to grow and amazingly productive.
Because plants can reach 3 to 9 feet in height, wide spacing between rows (6 inches is recommended) may make plants susceptible to lodging. With adequate moisture, temperature and fertility, researchers have recorded a growth rate of 1 foot per week. Plants can return to or exceed this growth rate if slowed by temporary drought.
Planting Directions
SOWING TEMPERATURE
70F - 95F
SEEDING RATE
30 - 90 lbs per acre
AVERAGE GERMINATION TIME
7 - 10 days
PLANTING DEPTH
1/2 - 1 inch
SOWING METHOD
Broadcast or drill
ENVIRONMENT
Full sun to partial shade
USDA ZONES
5 - 10
ESTABLISHMENT RATE
Fast









Cowpeas (Vigna Unguiculata) - Cowpeas grow 24 - 36 inches tall and are very heat and drought tolerant. They are very hardy, making them an excellent choice for food plots in the southern United States. Deer, pheasant, turkey, quail and other wildlife eagerly seek out the foliage and grain produced by cowpeas as they grow to maturity. Other animals such as: cattle, hogs, poultry, goats and other upland game birds will also enjoy feeding on cowpeas.
Cowpeas are the most heat loving legume found in the United States. They thrive in hot, moist climates, but are also very drought tolerant. Adapted to a wide range of soil types. Commonly used by farmers for silage and as a cover crop, but also widely planted as a high protein forage. Cowpeas are adapted to a wide range of soils, but prefers well drained soils with a pH between 6.0 - 7.0. Like all cowpeas, they can be consumed by humans in the form of snap beans and dry beans.
Cowpeas are perennial in USDA Zones 7 - 10, but are often grown in the midwest as an annual in USDA Zone 5 and 6.
Seeding Rate: 30 - 90 lbs per acre
Planting Depth: 1/2 - 1 inch deep
Planting Directions
SOWING TEMPERATURE
50F+
SEEDING RATE
20 - 30 lbs per acre
AVERAGE GERM TIME
7 - 14 days
PLANTING DEPTH
1/4 - 1/2 inch
SOWING METHOD
Broadcast or drill
ENVIRONMENT
Full sun
USDA ZONES
3 - 9
ESTABLISHMENT RATE
Fast
WHEN TO PLANT
Spring to late summer









White Cloud Crimson Clover (Trifolium Incarnatum) - White Cloud crimson clover is the only white flowered Trifolium incarnatum cultivar in the US. White Cloud is truly white with white seeds. With a lack of red coloration, there are lower levels of bitter anthocyanins thus making it a sweeter clover so palatability and intake should be higher. Though not statistically quantified, anecdotal evidence have shown that White Cloud is preferred by livestock and wildlife over other palatable forage.
Use this unique crimson clover for hay, pasture, silage, livestock, forage, wildlife food plots, cover crops, green manure crops, crop rotations, nitrogen fixator, and for a ground cover. White Cloud is adapted to any region where crimson clover is used for cover crops, whether spring or fall sown. Its high dry matter yield and the ability of annual clovers to fix nitrogen makes White Cloud a great choice for cover crop or rotation/green manure applications.
Seeding Rate: 20 - 25 lbs per acre for broadcast seeding
Inoculated Seed - We now offer White Cloud crimson clover seed that has been coated with an inoculant for better establishment. Rhizobium strains are specifically chosen for each seed type. A key to any successful establishment and early seed development is moisture. This coating with inoculant is naturally water absorbent and helps attract soil moisture to the seed, getting your stand established quickly. This coating process which Outsidepride utilizes, assures that only the top-performing and crop-specific rhizobia will be applied to ensure your clovers reach maximum nodulation, stand establishment, and yield potential. The weight of the clover seeds will contain approximately 50% coating material that contains the inoculant and water holding material for better establishment and viability of the seed. There is no difference in the seeding rates between the coated and raw seed due to the increased germination and viability of the bulk clover seeds that are coated and inoculated.
Planting Directions
SOWING TEMPERATURE
41F+
SEEDING RATE
1 - 2 lbs per 1,000 square feet
AVERAGE GERMINATION TIME
7 - 14 days
PLANTING DEPTH
1 - 2 inches
SOWING METHOD
Broadcast or drill
ENVIRONMENT
Full sun
USDA ZONES
2 - 10
ESTABLISHMENT RATE
Fast








Fava Beans (Vicia Faba) - A relative of vetch, fava beans have erect, coarse stems and large leaves that grow into a bushy plant. This annual legume is also known as broad bean, field bean, horse bean, and Fababean. There are many varieties, even one for human consumption which is called Windsor bean. The cultivation of the bean dates back to early history where it is native to the Mediterranean region, especially Italy and Iran. In North America, Canada is the largest producer of Fava bean since they produce best in cool summer climates.
Our Fava beans are forage quality. They are not for human consumption.
































