-
CATEGORY ::
- All Seeds /
- All Herb Seeds /
- All Basil Seeds







Basil Sweet Genovese Herb & Microgreens Seeds
SEEDING RATE
0.35 oz per 10 x 20 Tray
TB seed /1 - 2 Cup Sprouts
GROWING MEDIUMS
Hydroponic or Soil
PRESOAK
No
BLACKOUT TIME
4 - 7 Days
SPROUTING METHODS
Tray, Sack or Jar
SPROUTING HARVEST
14 - 21 Days
MICROGREENS HARVEST
22 - 30 Days
BABY GREENS HARVEST
31 - 40 Days
FLAVOR PROFILE
Intense Basil, Sweet
About...
(Ocimum basilicum genovese) - Today, basil is a staple in cuisines worldwide, particularly in Italian and Southeast Asian dishes. It’s the main ingredient in pesto, a crucial element in Thai curries, and a flavorful addition to salads, soups, and pizzas. Basil contains many nutritional benefits. It's not just great tasting and a wonderful addition to culinary recipes, it is full of antioxidants. You might think that a smaller plant means a smaller flavor, but that’s definitely not the case here. Genovese basil microgreens actually have a stronger taste than mature basil, are slightly sweeter, and more tender. Read More....MORE BASIL OPTIONS
Planting Directions
TEMPERATURE
60F
AVERAGE GERM TIME
7 - 14 days
LIGHT REQUIRED
Yes
DEPTH
1/4 inch
SOWING RATE
5 - 6 seeds per inch
MOISTURE
Keep seeds moist until germination
PLANT SPACING
Rows 18 inches apart; thin seedlings 8 inches
Microgreen Information
NUTRIENTS
Vitamins A , B, C, E, and K, Calcium, Choline, Iron, Magnesium, Manganese, Niacin, Phosphorus, Potassium, Zinc, Antioxidants
MICROGREEN TEXTURE
Succulent, crisp, fresh
COMMON USES
Soups, salads, pasta
Microgreens Planting Guide









(Continued From Top) - In its microgreen form, basil retains its medicinal properties. It packs an even denser nutritional punch, making it a valuable addition to any diet. They are typically harvested before they reach 3 inches in height since they taste better when slightly smaller. Basil microgreens are among the microgreens with the slowest growth rates. They will still be grown in a few weeks, of course.
Genovese bsil is a unique seed in that it develops a jelly-like coating when it gets wet. To aid with germination, mist more frequently to keep the coating moist. Grows very well hydroponically and does better in well-lit conditions, but it is a slower grower. You may experiment with harvest times past 10 days. Genovese basil is a beautiful green color with an interesting shape that makes for a colorful garnish. Micro basil does not grow tall, so you will need to harvest close to the root line and rinse well.
This variety of Sweet Basil seeds produce extremely tender and fragrant herb plants. Genovese Basil has extra-large, dark green leaves and is often used in Italian pesto. Genovese Basil typically grows to a height of 18 - 24 inches. Plant Genovese Basil seeds indoors or directly sow the herb seeds outside after all danger of frost. Like most Basil plants, it grows best in full sun. When you plant these herb seeds in nice, warm temperatures, it only takes 60 - 90 days for full maturity.
Genovese Sweeet Basil plants are characterized by edible aromatic foliage. The leaves are dark green and approximately 3 inches long. This Basil herb plant has abundant leaves with authentic Italian Basil flavor that tastes great in a pesto sauce. Genovese Basil plants love the sun and cannot tolerate cold. If you are keeping it indoors to extend its growing season, make sure it gets lots of sunlight and adequate water. You may want to pinch the flowering tops down to the first set of leaves to prolong the use of this Basil plant in the kitchen.
Harvesting: Basil leaves can be harvested as soon as they reach a height of 3 inches. The best time to harvest the leaves is in the morning after the dew dries. After the plant is established, harvesting often actually improves production; once the flowers develop, however, the leaves grow bitter to the taste. Remove single leaves or parts of a stem as needed, taking care to leave at least three sets of leaves on the length of the stem for healthy growth. When harvesting, pinch off the stem directly above the next set of leaves. Fresh basil will keep for several days at room temperature, with the stems in a glass of water; if refrigerated, it tends to wilt and turn brown. Basil also freezes and dries well. Since the water content of basil is very high and it can mold easily, the best method for drying is a dehydrator, an oven, or a similar dry, warm location.
Note: Our seeds are perfect for growing both indoors and outdoors, allowing you to nurture your own green space regardless of the season. They are versatile, enabling you to germinate plants anytime, anywhere, whether it's inside your home or outside in your garden, opening up new possibilities for your gardening endeavors.
Common Questions
Which herbs can thrive in the kitchen?
Not all herbs are suitable for indoor growth. Herbs with woody, bushy growth, like rosemary are too large for indoor herb gardens. Consider other more suitable herbs for an indoor kitchen garden, such as chives, oregano, thyme, dill, mint, basil, cilantro, sage and savory. Each herb has specific growing needs, so ensure to provide the right amount of light, humidity, and air circulation. If using a single large container, ensure that all plants require similar amounts of sunlight and water. For instance, chives and cilantro may not need as much sunlight as dill and oregano.
What are good companion plants for herb gardens?
Pairing herbs based on watering requirements, like planting lavender with thyme or basil with chives, is ideal for maintaining the health of both plants. Avoid companion planting with catnip, lemon balm and mint as they should be grown in separate pots due to their rapid spreading nature that can overtake other plants in your indoor herb garden.
When do I establish an indoor herb garden?
Create a kitchen herb garden by propagating cuttings from your outdoor plants as the weather cools in the fall. If you opt to sow your indoor herb garden from purchased seeds, begin a few weeks before the anticipated first frost of the season. Most herbs can be harvested within a few weeks, so there is no need to plant too far in advance.
Do kitchen herbs need full sun?
Most herbs need 6 hours of sunlight a day to thrive. If you do not have this type of light available in your kitchen, consider a grow light that will run 14-16 hours per day 6 to 12 inches above your plants. NOTE: Rotate herbs periodically when grown in windows to let each part of the plant receive sunlight.
What time of year should you plant herbs?
Herbs grown in indoor gardens can be planted any time of year. Many gardeners prefer to grow their herbs outdoors during the summer growing season, and then move them to their indoor garden before the first frost of fall. If you prefer to start your seeds outdoors, you will need to wait until after danger of frost in the spring or start your seeds indoors 6 -8 weeks before last frost and transplant in your garden after danger of frost.
Do herbs come back every year?
Perennial herbs will come back each year when planted in the correct zone or grown indoors during the cold winter months. Popular perennial herbs are oregano, parsley, sage, fennel, chives, lavender, thyme and mint varieties.
How do I know when my herbs need watered?
Allow the soil to dry out just slightly before watering your herbs again. Give your indoor herb garden a dose of diluted water-soluble fertilizer every 2 weeks or so. Too much food will compromise the taste of the herbs. It is also beneficial to provide adequate humidity. If the indoor air is especially dry – which is often the case in regions with cold winters. Set the herbs pots on trays of stones. Fill the trays with water but keep the level below the drainage holes of your pots.
When do I water my outdoor herb garden?
Different herb plants will need different amounts of water so keep this in mind when planting your garden and keep similar plants together to simplify watering. Watering is best done in the early morning hours when temperatures are cooler. Many herbs are hardy. They can tolerate soil that is moderately dry. You want to keep an eye out for wilting when the soil is wet. Ideally, your herbs should make quick use of the water you give them. Saturated soil is not what you are after. Pay close attention to the coloration of the leaves on your herbs. Yellow leaves can be a sign of too much water, and so can black leaves. If you spot any mildew or fuzz on the herbs, too much moisture can be the problem.
How do I harvest my herbs?
Trim back flowering sections before they bloom for healthier leaves. Prune new growth on young plants weekly to encourage a fuller mature plant. Snip herbs for harvest when they are just a few inches tall. Pruning back the herbs often means a larger, longer harvest. Cut the new growth back at least one per week, even if you are not using the herbs in recipes (see drying and freezing page if you do not want to waste your harvest). Long stems that are about to set flower buds should be trimmed off as they appear.
What do I need to start an indoor herb garden?
Common tools needed for an indoor herb garden are: garden trowel, scissors for snipping, stones (optional). Materials for your herbs plants include seed, pots, potting soil, cactus potting soil (optional), pots or trays, fertilizer and a grow light if you do not have adequate sunlight of at least 6 hours per day for your plants.
How do I prepare my containers for planting?
Choose large, deep containers with drainage holes to accommodate fast-growing herbs. Fill the container with potting mix leaving about ½ inch clear at the top. Use standard commercial potting soil for most herbs but blend in cactus potting mix for herbs native to the Mediterranean, such as thyme and oregano which prefer dryer soils.
Can I put my indoor herb containers outside?
Yes! Move your potted herbs to the patio or deck when the weather warms in the spring and for a boost of sunshine.
How do I know when my herbs need larger containers?
When roots begin to emerge through the drainage holes of its container, it is time to repot the herbs. Replace the potting mix; the organic material in the potting mix breaks down over time. Remove any plants with woody or thickened stems and replace them with new seeds or seedlings.
Do herbs need fertilizer?
The short answer is yes. However, not all herbs have the same fertilizer needs. Herbs roughly fall into two groups. 1. Slow-growing herbs with small leaves or needles and fibrous, woody stems that are native to the mediterranean where they grow culinary lavender, month, marjoram, oregano, rosemary, sage, savory, tarragon and thyme. 2. Fast-growing herbs with larger, thinner leaves. These can be annuals such as basil, borage, cilantro, chervil and dill; bi-annual herbs such as parsley or perennials such as chives. Herbs in the first group generally need less fertilizer than herbs in the second group.
What type of nutrients do herbs need?
Start out by planting herbs in healthy soil rich in organic matter. In addition, they will benefit from an organic complete, slow-release fertilizer containing equal amounts of macronutrients nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. A slow-release fertilizer is especially important if your garden has sandy soil because nutrients wash out quickly. To give fast-growing herbs that you harvest often an extra boost, you can also apply fish emulsion, an organic fertilizer that is high in nitrogen, with an NPK ratio of 4-1-1 or 5-1-1.
How often should I fertilize my herbs?
The frequency of fertilization follows the growth pattern of the herbs. In soil of average fertility, it is usually sufficient to apply a balanced fertilizer in the spring when they break dormancy, or when the new growing season starts. For other herbs, a light monthly application of a slow-release complete fertilizer should be enough – unless the leaves start to look yellow, which may be a sign of nitrogen deficiency. In that case, applying fish emulsion is a quick fix but before you reach for the fertilizer bottle, rule out that the yellowing of leaves is not caused by something else.
How do I fertilize my herbs in a container?
Herbs grown in containers need fertilizer applications more often, because with frequent watering that container plants require, the fertilizer in the potting mix washes out more quickly. Just as with sandy soil, it is important to use slow-release fertilizer. The roots of container plants are in a confined space, unlike herbs grown in the garden or raised beds, which can lead to over fertilization if you are not careful. Organic fertilizers are recommended over synthetic which often contain a high level of salts that can build up in the container over time. To prevent this, it is best to use half the strength of the fertilizer amount specified on the label for any type of fertilizer.
Is it possible to overfertilize herbs?
Adding too much fertilizer to herbs usually leads to an excess of nitrogen, which has undesirable results especially for slow-growing herbs. For basil and other thin-leaved herbs, the fast leaf growth induced by nitrogen is fine because you want your plants to be lush. For rosemary and other Mediterranean herbs however, rapid growth means that there is less concentration of essential oils causing the herbs to become less aromatic and have weaker flavor.
How do I prepare garden soil before planting an herb garden?
Once you have picked the location for growing your herb garden, you will need to prepare the soil. If the soil is sandy or clay heavy, add plenty of compost. Even if your soil is in pretty good condition, working some compost into the soil will help provide nutrients to the herbs while they are growing.
Can I harvest my herbs too often?
Many times, when a new gardener is starting an herb garden, they are afraid that harvesting the herbs frequently will hurt them. The opposite is true. Frequent harvesting of herbs will result in the herb plant producing more and more foliage, which increases the amount you are able to harvest. At the end of the season, you can dry or freeze your herb harvest to enjoy home grown herbs all year long.
I don’t have a good sunny spot outdoors for my herb garden, what can I do?
If your yard is mostly shaded, there is not much you can do to change that, but you can pick shade friendly herbs. Parsley, sweet woodruff and mint are good examples of herbs that don’t require as much light. If you are growing plants in low light, manage your expectations. Your herbs will grow but will be slow and results less impressive.
My container soil is staying wet, what do I do?
Choose a container that allow for water to drain. If you over water or if it rains too much a good pot will allow the water to flow to the bottom without soaking and rotting the roots of your plants. You can use rocks or pottery shards to fill the bottom of the container to help with drainage. This applies outdoors too. If your herbs constantly have wet feet, they won’t thrive. Either plan when planting your garden and add some sand for drainage or pick plants that don’t mind wet roots as much.
My herbs plants are going to seed, why?
The short answer is you are not pruning enough. To prevent rapid growth and encourage a bushy habit, be sure to prune your herb plants regularly. The more you pick off your stems and leaves the longer your herb plant will remain in its production cycle. If you start to see flower heads, snip them right away. When you fail to cut back the plant, it is likely to go to seed and complete its lifecycle. Once that happens, many plants die back. Keep cutting and pinching back flowers to prevent this from happening.
Should I throw away my seeds on their expiration date?
Seeds do not have an expiration date, rather they are a sell by date just like food. The dates on seed packages are guidelines to help you know when your seeds are getting old, but it does not mean you need to toss them. Every plant is different. Some seeds last longer than others. Most seeds, if kept cool and dry, will last 2 – 3 years. If you are unsure test them out by growing microgreens.
Planting Directions
TEMPERATURE
60F
AVERAGE GERM TIME
5 - 10 days
LIGHT REQUIRED
Yes
DEPTH
1/4 inch
SOWING RATE
5 - 6 seeds per inch
MOISTURE
Keep moist until germination
PLANT SPACING
Rows 18 inches a part; thin seedlings 8 inches
PLANTING & CARE GUIDE









Thai Basil (Ocimum Basilicum Thai Siam Queen) - What a gorgeous addition for the herb garden that can easily be grown from Basil seeds! Thai Siam Queen Basil is as flavorful as it is attractive. The sturdy stems support extra-large, 4-inch-long and 2-inch-wide bright green leaves. Clusters of purple flowers are produced on the very top of the plant for a highly ornamental effect. Basil Siam Queen is loaded with spicy flavor and aroma that is a perfect addition to tomato dishes, pasta sauces, vegetables and soup. Basil is at its most flavorful when fresh. The best time to harvest is just as the plant starts to set flower buds, well before flowers bloom. For harvesting, cut stems just before flowers open, strip leaves and use fresh, or dry on tray in dark, airy place. Leaves may be frozen. Harvest Thai Siam Queen leaves continually to encourage new growth.
Grow the Thai Basil herb plant in a rich, well-drained soil in full sun, where the plant will reach 24 inches tall. Pinch out growing tips to encourage bushier plants and to delay flowering. Basil can be planted in the vegetable garden next to the tomatoes and the peppers as a companion plant to repel aphids, mites and tomato hornworms.
How To Grow Basil From Herb Seed: Start Basil seeds indoors near a sunny window 4 - 8 weeks before transplanting to the garden after danger of last frost. Or for areas with a long growing-season, sow Thai Basil seeds in garden in full sun when frost danger is over and ground is warm. Make shallow furrows and cover the herb seeds 1/4 inch with loose soil. Keep moist until germination. Approximate Seeds Per Ounce: 20,000
1997 AAS Edible Vegetable Winner. Siam Queen is an improved Thai basil or tropical basil. Prized for both culinary use and ornamental plant quality. Highly aromatic with licorice basil aroma. The late flowering, mature plant reaches about 2 feet in height and width. In many Thai dishes, Thai basil is added last, just prior to serving for its fragrance and flavor.
Common Questions
Which herbs can thrive in the kitchen?
Not all herbs are suitable for indoor growth. Herbs with woody, bushy growth, like rosemary are too large for indoor herb gardens. Consider other more suitable herbs for an indoor kitchen garden, such as chives, oregano, thyme, dill, mint, basil, cilantro, sage and savory. Each herb has specific growing needs, so ensure to provide the right amount of light, humidity, and air circulation. If using a single large container, ensure that all plants require similar amounts of sunlight and water. For instance, chives and cilantro may not need as much sunlight as dill and oregano.
What are good companion plants for herb gardens?
Pairing herbs based on watering requirements, like planting lavender with thyme or basil with chives, is ideal for maintaining the health of both plants. Avoid companion planting with catnip, lemon balm and mint as they should be grown in separate pots due to their rapid spreading nature that can overtake other plants in your indoor herb garden.
When do I establish an indoor herb garden?
Create a kitchen herb garden by propagating cuttings from your outdoor plants as the weather cools in the fall. If you opt to sow your indoor herb garden from purchased seeds, begin a few weeks before the anticipated first frost of the season. Most herbs can be harvested within a few weeks, so there is no need to plant too far in advance.
Do kitchen herbs need full sun?
Most herbs need 6 hours of sunlight a day to thrive. If you do not have this type of light available in your kitchen, consider a grow light that will run 14-16 hours per day 6 to 12 inches above your plants. NOTE: Rotate herbs periodically when grown in windows to let each part of the plant receive sunlight.
What time of year should you plant herbs?
Herbs grown in indoor gardens can be planted any time of year. Many gardeners prefer to grow their herbs outdoors during the summer growing season, and then move them to their indoor garden before the first frost of fall. If you prefer to start your seeds outdoors, you will need to wait until after danger of frost in the spring or start your seeds indoors 6 -8 weeks before last frost and transplant in your garden after danger of frost.
Do herbs come back every year?
Perennial herbs will come back each year when planted in the correct zone or grown indoors during the cold winter months. Popular perennial herbs are oregano, parsley, sage, fennel, chives, lavender, thyme and mint varieties.
How do I know when my herbs need watered?
Allow the soil to dry out just slightly before watering your herbs again. Give your indoor herb garden a dose of diluted water-soluble fertilizer every 2 weeks or so. Too much food will compromise the taste of the herbs. It is also beneficial to provide adequate humidity. If the indoor air is especially dry – which is often the case in regions with cold winters. Set the herbs pots on trays of stones. Fill the trays with water but keep the level below the drainage holes of your pots.
When do I water my outdoor herb garden?
Different herb plants will need different amounts of water so keep this in mind when planting your garden and keep similar plants together to simplify watering. Watering is best done in the early morning hours when temperatures are cooler. Many herbs are hardy. They can tolerate soil that is moderately dry. You want to keep an eye out for wilting when the soil is wet. Ideally, your herbs should make quick use of the water you give them. Saturated soil is not what you are after. Pay close attention to the coloration of the leaves on your herbs. Yellow leaves can be a sign of too much water, and so can black leaves. If you spot any mildew or fuzz on the herbs, too much moisture can be the problem.
How do I harvest my herbs?
Trim back flowering sections before they bloom for healthier leaves. Prune new growth on young plants weekly to encourage a fuller mature plant. Snip herbs for harvest when they are just a few inches tall. Pruning back the herbs often means a larger, longer harvest. Cut the new growth back at least one per week, even if you are not using the herbs in recipes (see drying and freezing page if you do not want to waste your harvest). Long stems that are about to set flower buds should be trimmed off as they appear.
What do I need to start an indoor herb garden?
Common tools needed for an indoor herb garden are: garden trowel, scissors for snipping, stones (optional). Materials for your herbs plants include seed, pots, potting soil, cactus potting soil (optional), pots or trays, fertilizer and a grow light if you do not have adequate sunlight of at least 6 hours per day for your plants.
How do I prepare my containers for planting?
Choose large, deep containers with drainage holes to accommodate fast-growing herbs. Fill the container with potting mix leaving about ½ inch clear at the top. Use standard commercial potting soil for most herbs but blend in cactus potting mix for herbs native to the Mediterranean, such as thyme and oregano which prefer dryer soils.
Can I put my indoor herb containers outside?
Yes! Move your potted herbs to the patio or deck when the weather warms in the spring and for a boost of sunshine.
How do I know when my herbs need larger containers?
When roots begin to emerge through the drainage holes of its container, it is time to repot the herbs. Replace the potting mix; the organic material in the potting mix breaks down over time. Remove any plants with woody or thickened stems and replace them with new seeds or seedlings.
Do herbs need fertilizer?
The short answer is yes. However, not all herbs have the same fertilizer needs. Herbs roughly fall into two groups. 1. Slow-growing herbs with small leaves or needles and fibrous, woody stems that are native to the mediterranean where they grow culinary lavender, month, marjoram, oregano, rosemary, sage, savory, tarragon and thyme. 2. Fast-growing herbs with larger, thinner leaves. These can be annuals such as basil, borage, cilantro, chervil and dill; bi-annual herbs such as parsley or perennials such as chives. Herbs in the first group generally need less fertilizer than herbs in the second group.
What type of nutrients do herbs need?
Start out by planting herbs in healthy soil rich in organic matter. In addition, they will benefit from an organic complete, slow-release fertilizer containing equal amounts of macronutrients nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. A slow-release fertilizer is especially important if your garden has sandy soil because nutrients wash out quickly. To give fast-growing herbs that you harvest often an extra boost, you can also apply fish emulsion, an organic fertilizer that is high in nitrogen, with an NPK ratio of 4-1-1 or 5-1-1.
How often should I fertilize my herbs?
The frequency of fertilization follows the growth pattern of the herbs. In soil of average fertility, it is usually sufficient to apply a balanced fertilizer in the spring when they break dormancy, or when the new growing season starts. For other herbs, a light monthly application of a slow-release complete fertilizer should be enough – unless the leaves start to look yellow, which may be a sign of nitrogen deficiency. In that case, applying fish emulsion is a quick fix but before you reach for the fertilizer bottle, rule out that the yellowing of leaves is not caused by something else.
How do I fertilize my herbs in a container?
Herbs grown in containers need fertilizer applications more often, because with frequent watering that container plants require, the fertilizer in the potting mix washes out more quickly. Just as with sandy soil, it is important to use slow-release fertilizer. The roots of container plants are in a confined space, unlike herbs grown in the garden or raised beds, which can lead to over fertilization if you are not careful. Organic fertilizers are recommended over synthetic which often contain a high level of salts that can build up in the container over time. To prevent this, it is best to use half the strength of the fertilizer amount specified on the label for any type of fertilizer.
Is it possible to overfertilize herbs?
Adding too much fertilizer to herbs usually leads to an excess of nitrogen, which has undesirable results especially for slow-growing herbs. For basil and other thin-leaved herbs, the fast leaf growth induced by nitrogen is fine because you want your plants to be lush. For rosemary and other Mediterranean herbs however, rapid growth means that there is less concentration of essential oils causing the herbs to become less aromatic and have weaker flavor.
How do I prepare garden soil before planting an herb garden?
Once you have picked the location for growing your herb garden, you will need to prepare the soil. If the soil is sandy or clay heavy, add plenty of compost. Even if your soil is in pretty good condition, working some compost into the soil will help provide nutrients to the herbs while they are growing.
Can I harvest my herbs too often?
Many times, when a new gardener is starting an herb garden, they are afraid that harvesting the herbs frequently will hurt them. The opposite is true. Frequent harvesting of herbs will result in the herb plant producing more and more foliage, which increases the amount you are able to harvest. At the end of the season, you can dry or freeze your herb harvest to enjoy home grown herbs all year long.
I don’t have a good sunny spot outdoors for my herb garden, what can I do?
If your yard is mostly shaded, there is not much you can do to change that, but you can pick shade friendly herbs. Parsley, sweet woodruff and mint are good examples of herbs that don’t require as much light. If you are growing plants in low light, manage your expectations. Your herbs will grow but will be slow and results less impressive.
My container soil is staying wet, what do I do?
Choose a container that allow for water to drain. If you over water or if it rains too much a good pot will allow the water to flow to the bottom without soaking and rotting the roots of your plants. You can use rocks or pottery shards to fill the bottom of the container to help with drainage. This applies outdoors too. If your herbs constantly have wet feet, they won’t thrive. Either plan when planting your garden and add some sand for drainage or pick plants that don’t mind wet roots as much.
My herbs plants are going to seed, why?
The short answer is you are not pruning enough. To prevent rapid growth and encourage a bushy habit, be sure to prune your herb plants regularly. The more you pick off your stems and leaves the longer your herb plant will remain in its production cycle. If you start to see flower heads, snip them right away. When you fail to cut back the plant, it is likely to go to seed and complete its lifecycle. Once that happens, many plants die back. Keep cutting and pinching back flowers to prevent this from happening.
Should I throw away my seeds on their expiration date?
Seeds do not have an expiration date, rather they are a sell by date just like food. The dates on seed packages are guidelines to help you know when your seeds are getting old, but it does not mean you need to toss them. Every plant is different. Some seeds last longer than others. Most seeds, if kept cool and dry, will last 2 – 3 years. If you are unsure test them out by growing microgreens.
Planting Directions
TEMPERATURE
60F
AVERAGE GERM TIME
7 - 21 days
LIGHT REQUIRED
Yes
DEPTH
1/4 inch
SOWING RATE
5 - 6 seeds per inch
MOISTURE
Keep moist until germination
PLANT SPACING
Rows 18 inches a part; thin seedlings 6 inches









Sweet Basil Large Leaved (Ocimum Basilicum Large Leaf) - Large Leaf Sweet Basil is regarded as the essential variety for true Neapolitan cuisine, especially pesto. Sweet Basil plants are loaded with volatile oils, responsible for the heady aroma and strong flavor so essential to cooking. Like all Basil plants, Sweet Large Leaf Basil is easy to establish from herb seeds for the garden or to grow in a container on the patio.
This Basil grows 18 to 24 inches high and 12 to 15 inches wide. The dark green, shiny leaves grow up to 3 inches long. Pick the extra large leaves and use them fresh or dried in tomato dishes, pasta sauces, vegetables and soups. Basil is at its most flavorful when fresh. The best time to harvest is just as the plant starts to set flower buds, well before flowers bloom. Harvest leaves continually to encourage new growth. Pinch out growing tips to encourage bushier plants and to delay flowering.
How To Grow Basil From Seed: Sow Basil seeds in the garden after all danger of frost has passed. For areas with short growing seasons, start the herb seeds indoors 4 - 8 weeks before setting out. Grow the Italian Basil herb in a rich, well-drained, soil and in full sun. Plant Basil in the vegetable garden next to the tomatoes and peppers as a companion plant to repel aphids, mites, and tomato hornworms.
Approximate Seeds Per Ounce: 10,000
Common Questions
Which herbs can thrive in the kitchen?
Not all herbs are suitable for indoor growth. Herbs with woody, bushy growth, like rosemary are too large for indoor herb gardens. Consider other more suitable herbs for an indoor kitchen garden, such as chives, oregano, thyme, dill, mint, basil, cilantro, sage and savory. Each herb has specific growing needs, so ensure to provide the right amount of light, humidity, and air circulation. If using a single large container, ensure that all plants require similar amounts of sunlight and water. For instance, chives and cilantro may not need as much sunlight as dill and oregano.
What are good companion plants for herb gardens?
Pairing herbs based on watering requirements, like planting lavender with thyme or basil with chives, is ideal for maintaining the health of both plants. Avoid companion planting with catnip, lemon balm and mint as they should be grown in separate pots due to their rapid spreading nature that can overtake other plants in your indoor herb garden.
When do I establish an indoor herb garden?
Create a kitchen herb garden by propagating cuttings from your outdoor plants as the weather cools in the fall. If you opt to sow your indoor herb garden from purchased seeds, begin a few weeks before the anticipated first frost of the season. Most herbs can be harvested within a few weeks, so there is no need to plant too far in advance.
Do kitchen herbs need full sun?
Most herbs need 6 hours of sunlight a day to thrive. If you do not have this type of light available in your kitchen, consider a grow light that will run 14-16 hours per day 6 to 12 inches above your plants. NOTE: Rotate herbs periodically when grown in windows to let each part of the plant receive sunlight.
What time of year should you plant herbs?
Herbs grown in indoor gardens can be planted any time of year. Many gardeners prefer to grow their herbs outdoors during the summer growing season, and then move them to their indoor garden before the first frost of fall. If you prefer to start your seeds outdoors, you will need to wait until after danger of frost in the spring or start your seeds indoors 6 -8 weeks before last frost and transplant in your garden after danger of frost.
Do herbs come back every year?
Perennial herbs will come back each year when planted in the correct zone or grown indoors during the cold winter months. Popular perennial herbs are oregano, parsley, sage, fennel, chives, lavender, thyme and mint varieties.
How do I know when my herbs need watered?
Allow the soil to dry out just slightly before watering your herbs again. Give your indoor herb garden a dose of diluted water-soluble fertilizer every 2 weeks or so. Too much food will compromise the taste of the herbs. It is also beneficial to provide adequate humidity. If the indoor air is especially dry – which is often the case in regions with cold winters. Set the herbs pots on trays of stones. Fill the trays with water but keep the level below the drainage holes of your pots.
When do I water my outdoor herb garden?
Different herb plants will need different amounts of water so keep this in mind when planting your garden and keep similar plants together to simplify watering. Watering is best done in the early morning hours when temperatures are cooler. Many herbs are hardy. They can tolerate soil that is moderately dry. You want to keep an eye out for wilting when the soil is wet. Ideally, your herbs should make quick use of the water you give them. Saturated soil is not what you are after. Pay close attention to the coloration of the leaves on your herbs. Yellow leaves can be a sign of too much water, and so can black leaves. If you spot any mildew or fuzz on the herbs, too much moisture can be the problem.
How do I harvest my herbs?
Trim back flowering sections before they bloom for healthier leaves. Prune new growth on young plants weekly to encourage a fuller mature plant. Snip herbs for harvest when they are just a few inches tall. Pruning back the herbs often means a larger, longer harvest. Cut the new growth back at least one per week, even if you are not using the herbs in recipes (see drying and freezing page if you do not want to waste your harvest). Long stems that are about to set flower buds should be trimmed off as they appear.
What do I need to start an indoor herb garden?
Common tools needed for an indoor herb garden are: garden trowel, scissors for snipping, stones (optional). Materials for your herbs plants include seed, pots, potting soil, cactus potting soil (optional), pots or trays, fertilizer and a grow light if you do not have adequate sunlight of at least 6 hours per day for your plants.
How do I prepare my containers for planting?
Choose large, deep containers with drainage holes to accommodate fast-growing herbs. Fill the container with potting mix leaving about ½ inch clear at the top. Use standard commercial potting soil for most herbs but blend in cactus potting mix for herbs native to the Mediterranean, such as thyme and oregano which prefer dryer soils.
Can I put my indoor herb containers outside?
Yes! Move your potted herbs to the patio or deck when the weather warms in the spring and for a boost of sunshine.
How do I know when my herbs need larger containers?
When roots begin to emerge through the drainage holes of its container, it is time to repot the herbs. Replace the potting mix; the organic material in the potting mix breaks down over time. Remove any plants with woody or thickened stems and replace them with new seeds or seedlings.
Do herbs need fertilizer?
The short answer is yes. However, not all herbs have the same fertilizer needs. Herbs roughly fall into two groups. 1. Slow-growing herbs with small leaves or needles and fibrous, woody stems that are native to the mediterranean where they grow culinary lavender, month, marjoram, oregano, rosemary, sage, savory, tarragon and thyme. 2. Fast-growing herbs with larger, thinner leaves. These can be annuals such as basil, borage, cilantro, chervil and dill; bi-annual herbs such as parsley or perennials such as chives. Herbs in the first group generally need less fertilizer than herbs in the second group.
What type of nutrients do herbs need?
Start out by planting herbs in healthy soil rich in organic matter. In addition, they will benefit from an organic complete, slow-release fertilizer containing equal amounts of macronutrients nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. A slow-release fertilizer is especially important if your garden has sandy soil because nutrients wash out quickly. To give fast-growing herbs that you harvest often an extra boost, you can also apply fish emulsion, an organic fertilizer that is high in nitrogen, with an NPK ratio of 4-1-1 or 5-1-1.
How often should I fertilize my herbs?
The frequency of fertilization follows the growth pattern of the herbs. In soil of average fertility, it is usually sufficient to apply a balanced fertilizer in the spring when they break dormancy, or when the new growing season starts. For other herbs, a light monthly application of a slow-release complete fertilizer should be enough – unless the leaves start to look yellow, which may be a sign of nitrogen deficiency. In that case, applying fish emulsion is a quick fix but before you reach for the fertilizer bottle, rule out that the yellowing of leaves is not caused by something else.
How do I fertilize my herbs in a container?
Herbs grown in containers need fertilizer applications more often, because with frequent watering that container plants require, the fertilizer in the potting mix washes out more quickly. Just as with sandy soil, it is important to use slow-release fertilizer. The roots of container plants are in a confined space, unlike herbs grown in the garden or raised beds, which can lead to over fertilization if you are not careful. Organic fertilizers are recommended over synthetic which often contain a high level of salts that can build up in the container over time. To prevent this, it is best to use half the strength of the fertilizer amount specified on the label for any type of fertilizer.
Is it possible to overfertilize herbs?
Adding too much fertilizer to herbs usually leads to an excess of nitrogen, which has undesirable results especially for slow-growing herbs. For basil and other thin-leaved herbs, the fast leaf growth induced by nitrogen is fine because you want your plants to be lush. For rosemary and other Mediterranean herbs however, rapid growth means that there is less concentration of essential oils causing the herbs to become less aromatic and have weaker flavor.
How do I prepare garden soil before planting an herb garden?
Once you have picked the location for growing your herb garden, you will need to prepare the soil. If the soil is sandy or clay heavy, add plenty of compost. Even if your soil is in pretty good condition, working some compost into the soil will help provide nutrients to the herbs while they are growing.
Can I harvest my herbs too often?
Many times, when a new gardener is starting an herb garden, they are afraid that harvesting the herbs frequently will hurt them. The opposite is true. Frequent harvesting of herbs will result in the herb plant producing more and more foliage, which increases the amount you are able to harvest. At the end of the season, you can dry or freeze your herb harvest to enjoy home grown herbs all year long.
I don’t have a good sunny spot outdoors for my herb garden, what can I do?
If your yard is mostly shaded, there is not much you can do to change that, but you can pick shade friendly herbs. Parsley, sweet woodruff and mint are good examples of herbs that don’t require as much light. If you are growing plants in low light, manage your expectations. Your herbs will grow but will be slow and results less impressive.
My container soil is staying wet, what do I do?
Choose a container that allow for water to drain. If you over water or if it rains too much a good pot will allow the water to flow to the bottom without soaking and rotting the roots of your plants. You can use rocks or pottery shards to fill the bottom of the container to help with drainage. This applies outdoors too. If your herbs constantly have wet feet, they won’t thrive. Either plan when planting your garden and add some sand for drainage or pick plants that don’t mind wet roots as much.
My herbs plants are going to seed, why?
The short answer is you are not pruning enough. To prevent rapid growth and encourage a bushy habit, be sure to prune your herb plants regularly. The more you pick off your stems and leaves the longer your herb plant will remain in its production cycle. If you start to see flower heads, snip them right away. When you fail to cut back the plant, it is likely to go to seed and complete its lifecycle. Once that happens, many plants die back. Keep cutting and pinching back flowers to prevent this from happening.
Should I throw away my seeds on their expiration date?
Seeds do not have an expiration date, rather they are a sell by date just like food. The dates on seed packages are guidelines to help you know when your seeds are getting old, but it does not mean you need to toss them. Every plant is different. Some seeds last longer than others. Most seeds, if kept cool and dry, will last 2 – 3 years. If you are unsure test them out by growing microgreens.
Planting Directions
TEMPERATURE
60F
AVERAGE GERM TIME
7 - 14 days
LIGHT REQUIRED
Yes
DEPTH
1/4 inch
SOWING RATE
5 - 6 seeds per inch
MOISTURE
Keep moist until germination
PLANT SPACING
Rows 18 inches a part; thin seedlings 6 inches









Sweet Basil Dark Opal (Ocimum Basilicum Dark Opal) - Start these Sweet Basil seeds for both color as well as flavor. This Basil herb variety is called Dark Opal. The leaves have a clove-like spiciness flavor which is a little too strong for pesto but great for almost any basil dish, and it's especially good for vinegars and oils.
This old time favorite Dark Opal Sweet Basil herb has been delighting gardeners and foodies alike for decades now. Lots of people grow it for its decorative qualities, but it is a culinary wonder. Use its large glossy, purple leaves with large sliced tomatoes for fun contrast and a perfect flavor match that has been used since the turn of the last century! Dark Opal Basil grows best in full sun, but make sure it is fully protected from wind and the elements.
Grow in a rich, well-drained, soil in full sun. Pinch out growing tips to encourage bushier plants and to delay flowering. Start Basil seeds indoors near a sunny window 6 weeks before transplanting to the garden after danger of last frost. Or, sow Sweet Basil herb seeds in garden in full sun when frost danger is over and ground is warm. Make shallow furrows and cover the herb seeds 1/4 inch with loose soil. Keep seed moist until germination.
1962 AAS Edible Vegetable Winner. Stunning violet purple leaves and pink flowers make this variety perfect for flower beds and pots. The licorice flavor is ideal paired with tomatoes and the dark leaves color and flavor homemade bottles of vinegar. Shown to have resistance to downy mildew in university trials.
Common Questions
Which herbs can thrive in the kitchen?
Not all herbs are suitable for indoor growth. Herbs with woody, bushy growth, like rosemary are too large for indoor herb gardens. Consider other more suitable herbs for an indoor kitchen garden, such as chives, oregano, thyme, dill, mint, basil, cilantro, sage and savory. Each herb has specific growing needs, so ensure to provide the right amount of light, humidity, and air circulation. If using a single large container, ensure that all plants require similar amounts of sunlight and water. For instance, chives and cilantro may not need as much sunlight as dill and oregano.
What are good companion plants for herb gardens?
Pairing herbs based on watering requirements, like planting lavender with thyme or basil with chives, is ideal for maintaining the health of both plants. Avoid companion planting with catnip, lemon balm and mint as they should be grown in separate pots due to their rapid spreading nature that can overtake other plants in your indoor herb garden.
When do I establish an indoor herb garden?
Create a kitchen herb garden by propagating cuttings from your outdoor plants as the weather cools in the fall. If you opt to sow your indoor herb garden from purchased seeds, begin a few weeks before the anticipated first frost of the season. Most herbs can be harvested within a few weeks, so there is no need to plant too far in advance.
Do kitchen herbs need full sun?
Most herbs need 6 hours of sunlight a day to thrive. If you do not have this type of light available in your kitchen, consider a grow light that will run 14-16 hours per day 6 to 12 inches above your plants. NOTE: Rotate herbs periodically when grown in windows to let each part of the plant receive sunlight.
What time of year should you plant herbs?
Herbs grown in indoor gardens can be planted any time of year. Many gardeners prefer to grow their herbs outdoors during the summer growing season, and then move them to their indoor garden before the first frost of fall. If you prefer to start your seeds outdoors, you will need to wait until after danger of frost in the spring or start your seeds indoors 6 -8 weeks before last frost and transplant in your garden after danger of frost.
Do herbs come back every year?
Perennial herbs will come back each year when planted in the correct zone or grown indoors during the cold winter months. Popular perennial herbs are oregano, parsley, sage, fennel, chives, lavender, thyme and mint varieties.
How do I know when my herbs need watered?
Allow the soil to dry out just slightly before watering your herbs again. Give your indoor herb garden a dose of diluted water-soluble fertilizer every 2 weeks or so. Too much food will compromise the taste of the herbs. It is also beneficial to provide adequate humidity. If the indoor air is especially dry – which is often the case in regions with cold winters. Set the herbs pots on trays of stones. Fill the trays with water but keep the level below the drainage holes of your pots.
When do I water my outdoor herb garden?
Different herb plants will need different amounts of water so keep this in mind when planting your garden and keep similar plants together to simplify watering. Watering is best done in the early morning hours when temperatures are cooler. Many herbs are hardy. They can tolerate soil that is moderately dry. You want to keep an eye out for wilting when the soil is wet. Ideally, your herbs should make quick use of the water you give them. Saturated soil is not what you are after. Pay close attention to the coloration of the leaves on your herbs. Yellow leaves can be a sign of too much water, and so can black leaves. If you spot any mildew or fuzz on the herbs, too much moisture can be the problem.
How do I harvest my herbs?
Trim back flowering sections before they bloom for healthier leaves. Prune new growth on young plants weekly to encourage a fuller mature plant. Snip herbs for harvest when they are just a few inches tall. Pruning back the herbs often means a larger, longer harvest. Cut the new growth back at least one per week, even if you are not using the herbs in recipes (see drying and freezing page if you do not want to waste your harvest). Long stems that are about to set flower buds should be trimmed off as they appear.
What do I need to start an indoor herb garden?
Common tools needed for an indoor herb garden are: garden trowel, scissors for snipping, stones (optional). Materials for your herbs plants include seed, pots, potting soil, cactus potting soil (optional), pots or trays, fertilizer and a grow light if you do not have adequate sunlight of at least 6 hours per day for your plants.
How do I prepare my containers for planting?
Choose large, deep containers with drainage holes to accommodate fast-growing herbs. Fill the container with potting mix leaving about ½ inch clear at the top. Use standard commercial potting soil for most herbs but blend in cactus potting mix for herbs native to the Mediterranean, such as thyme and oregano which prefer dryer soils.
Can I put my indoor herb containers outside?
Yes! Move your potted herbs to the patio or deck when the weather warms in the spring and for a boost of sunshine.
How do I know when my herbs need larger containers?
When roots begin to emerge through the drainage holes of its container, it is time to repot the herbs. Replace the potting mix; the organic material in the potting mix breaks down over time. Remove any plants with woody or thickened stems and replace them with new seeds or seedlings.
Do herbs need fertilizer?
The short answer is yes. However, not all herbs have the same fertilizer needs. Herbs roughly fall into two groups. 1. Slow-growing herbs with small leaves or needles and fibrous, woody stems that are native to the mediterranean where they grow culinary lavender, month, marjoram, oregano, rosemary, sage, savory, tarragon and thyme. 2. Fast-growing herbs with larger, thinner leaves. These can be annuals such as basil, borage, cilantro, chervil and dill; bi-annual herbs such as parsley or perennials such as chives. Herbs in the first group generally need less fertilizer than herbs in the second group.
What type of nutrients do herbs need?
Start out by planting herbs in healthy soil rich in organic matter. In addition, they will benefit from an organic complete, slow-release fertilizer containing equal amounts of macronutrients nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. A slow-release fertilizer is especially important if your garden has sandy soil because nutrients wash out quickly. To give fast-growing herbs that you harvest often an extra boost, you can also apply fish emulsion, an organic fertilizer that is high in nitrogen, with an NPK ratio of 4-1-1 or 5-1-1.
How often should I fertilize my herbs?
The frequency of fertilization follows the growth pattern of the herbs. In soil of average fertility, it is usually sufficient to apply a balanced fertilizer in the spring when they break dormancy, or when the new growing season starts. For other herbs, a light monthly application of a slow-release complete fertilizer should be enough – unless the leaves start to look yellow, which may be a sign of nitrogen deficiency. In that case, applying fish emulsion is a quick fix but before you reach for the fertilizer bottle, rule out that the yellowing of leaves is not caused by something else.
How do I fertilize my herbs in a container?
Herbs grown in containers need fertilizer applications more often, because with frequent watering that container plants require, the fertilizer in the potting mix washes out more quickly. Just as with sandy soil, it is important to use slow-release fertilizer. The roots of container plants are in a confined space, unlike herbs grown in the garden or raised beds, which can lead to over fertilization if you are not careful. Organic fertilizers are recommended over synthetic which often contain a high level of salts that can build up in the container over time. To prevent this, it is best to use half the strength of the fertilizer amount specified on the label for any type of fertilizer.
Is it possible to overfertilize herbs?
Adding too much fertilizer to herbs usually leads to an excess of nitrogen, which has undesirable results especially for slow-growing herbs. For basil and other thin-leaved herbs, the fast leaf growth induced by nitrogen is fine because you want your plants to be lush. For rosemary and other Mediterranean herbs however, rapid growth means that there is less concentration of essential oils causing the herbs to become less aromatic and have weaker flavor.
How do I prepare garden soil before planting an herb garden?
Once you have picked the location for growing your herb garden, you will need to prepare the soil. If the soil is sandy or clay heavy, add plenty of compost. Even if your soil is in pretty good condition, working some compost into the soil will help provide nutrients to the herbs while they are growing.
Can I harvest my herbs too often?
Many times, when a new gardener is starting an herb garden, they are afraid that harvesting the herbs frequently will hurt them. The opposite is true. Frequent harvesting of herbs will result in the herb plant producing more and more foliage, which increases the amount you are able to harvest. At the end of the season, you can dry or freeze your herb harvest to enjoy home grown herbs all year long.
I don’t have a good sunny spot outdoors for my herb garden, what can I do?
If your yard is mostly shaded, there is not much you can do to change that, but you can pick shade friendly herbs. Parsley, sweet woodruff and mint are good examples of herbs that don’t require as much light. If you are growing plants in low light, manage your expectations. Your herbs will grow but will be slow and results less impressive.
My container soil is staying wet, what do I do?
Choose a container that allow for water to drain. If you over water or if it rains too much a good pot will allow the water to flow to the bottom without soaking and rotting the roots of your plants. You can use rocks or pottery shards to fill the bottom of the container to help with drainage. This applies outdoors too. If your herbs constantly have wet feet, they won’t thrive. Either plan when planting your garden and add some sand for drainage or pick plants that don’t mind wet roots as much.
My herbs plants are going to seed, why?
The short answer is you are not pruning enough. To prevent rapid growth and encourage a bushy habit, be sure to prune your herb plants regularly. The more you pick off your stems and leaves the longer your herb plant will remain in its production cycle. If you start to see flower heads, snip them right away. When you fail to cut back the plant, it is likely to go to seed and complete its lifecycle. Once that happens, many plants die back. Keep cutting and pinching back flowers to prevent this from happening.
Should I throw away my seeds on their expiration date?
Seeds do not have an expiration date, rather they are a sell by date just like food. The dates on seed packages are guidelines to help you know when your seeds are getting old, but it does not mean you need to toss them. Every plant is different. Some seeds last longer than others. Most seeds, if kept cool and dry, will last 2 – 3 years. If you are unsure test them out by growing microgreens.
Planting Directions
TEMPERATURE
60F
AVERAGE GERM TIME
5 - 14 days
LIGHT REQUIRED
Yes
DEPTH
1/4 inch
SOWING RATE
5 - 6 seeds per inch
MOISTURE
Keep moist until germination
PLANT SPACING
Rows 18 inches a part; thin seedlings 6 inches









Lemon Basil (Ocimum Basilicum Citriodorum) - This winning Basil offers a different scent - pure, clean, citrus-lemon, and it's easily grown from Basil seeds! Basil is an indispensable flavoring, and it's used around the world. Pick the leaves and use them fresh or dried in herb vinegars and with chicken, fish, vegetables and soups. There are really no rules when using Basil in the kitchen! You can also use Lemon Basil plants in the garden as a companion plant to repel aphids, mites, and tomato hornworms.
Lemon Basil herb plants are upright, bushy and grow 26 inches high and 10 to 14 inches wide. The narrow, ovate, light green leaves reach 2 inches long. Small blooms of white flowers are followed by lemon-scented seeds. Basil is at its most flavorful when fresh. The best time to harvest is just as the plant starts to set flower buds, well before flowers bloom. For harvesting, cut stems just before flowers open, strip leaves and use fresh, or dry on tray in dark, airy place. Leaves may be frozen.
How To Grow Lemon Basil From Herb Seed: Sow Basil seeds in the garden after all danger of frost has passed. For areas with short growing seasons, start herb seeds indoors 4 - 8 weeks before setting out. Grow Lemon Basil in a rich, well-drained, soil and in full sun. Pinch the tip from the center shoot of the Lemon Basil seedlings after they have grown for 6 weeks to force side growth and prevent early flowering. If flower stalks develop, simply snip them off.
Approximate Seeds Per Ounce: 25,000
Common Questions
Which herbs can thrive in the kitchen?
Not all herbs are suitable for indoor growth. Herbs with woody, bushy growth, like rosemary are too large for indoor herb gardens. Consider other more suitable herbs for an indoor kitchen garden, such as chives, oregano, thyme, dill, mint, basil, cilantro, sage and savory. Each herb has specific growing needs, so ensure to provide the right amount of light, humidity, and air circulation. If using a single large container, ensure that all plants require similar amounts of sunlight and water. For instance, chives and cilantro may not need as much sunlight as dill and oregano.
What are good companion plants for herb gardens?
Pairing herbs based on watering requirements, like planting lavender with thyme or basil with chives, is ideal for maintaining the health of both plants. Avoid companion planting with catnip, lemon balm and mint as they should be grown in separate pots due to their rapid spreading nature that can overtake other plants in your indoor herb garden.
When do I establish an indoor herb garden?
Create a kitchen herb garden by propagating cuttings from your outdoor plants as the weather cools in the fall. If you opt to sow your indoor herb garden from purchased seeds, begin a few weeks before the anticipated first frost of the season. Most herbs can be harvested within a few weeks, so there is no need to plant too far in advance.
Do kitchen herbs need full sun?
Most herbs need 6 hours of sunlight a day to thrive. If you do not have this type of light available in your kitchen, consider a grow light that will run 14-16 hours per day 6 to 12 inches above your plants. NOTE: Rotate herbs periodically when grown in windows to let each part of the plant receive sunlight.
What time of year should you plant herbs?
Herbs grown in indoor gardens can be planted any time of year. Many gardeners prefer to grow their herbs outdoors during the summer growing season, and then move them to their indoor garden before the first frost of fall. If you prefer to start your seeds outdoors, you will need to wait until after danger of frost in the spring or start your seeds indoors 6 -8 weeks before last frost and transplant in your garden after danger of frost.
Do herbs come back every year?
Perennial herbs will come back each year when planted in the correct zone or grown indoors during the cold winter months. Popular perennial herbs are oregano, parsley, sage, fennel, chives, lavender, thyme and mint varieties.
How do I know when my herbs need watered?
Allow the soil to dry out just slightly before watering your herbs again. Give your indoor herb garden a dose of diluted water-soluble fertilizer every 2 weeks or so. Too much food will compromise the taste of the herbs. It is also beneficial to provide adequate humidity. If the indoor air is especially dry – which is often the case in regions with cold winters. Set the herbs pots on trays of stones. Fill the trays with water but keep the level below the drainage holes of your pots.
When do I water my outdoor herb garden?
Different herb plants will need different amounts of water so keep this in mind when planting your garden and keep similar plants together to simplify watering. Watering is best done in the early morning hours when temperatures are cooler. Many herbs are hardy. They can tolerate soil that is moderately dry. You want to keep an eye out for wilting when the soil is wet. Ideally, your herbs should make quick use of the water you give them. Saturated soil is not what you are after. Pay close attention to the coloration of the leaves on your herbs. Yellow leaves can be a sign of too much water, and so can black leaves. If you spot any mildew or fuzz on the herbs, too much moisture can be the problem.
How do I harvest my herbs?
Trim back flowering sections before they bloom for healthier leaves. Prune new growth on young plants weekly to encourage a fuller mature plant. Snip herbs for harvest when they are just a few inches tall. Pruning back the herbs often means a larger, longer harvest. Cut the new growth back at least one per week, even if you are not using the herbs in recipes (see drying and freezing page if you do not want to waste your harvest). Long stems that are about to set flower buds should be trimmed off as they appear.
What do I need to start an indoor herb garden?
Common tools needed for an indoor herb garden are: garden trowel, scissors for snipping, stones (optional). Materials for your herbs plants include seed, pots, potting soil, cactus potting soil (optional), pots or trays, fertilizer and a grow light if you do not have adequate sunlight of at least 6 hours per day for your plants.
How do I prepare my containers for planting?
Choose large, deep containers with drainage holes to accommodate fast-growing herbs. Fill the container with potting mix leaving about ½ inch clear at the top. Use standard commercial potting soil for most herbs but blend in cactus potting mix for herbs native to the Mediterranean, such as thyme and oregano which prefer dryer soils.
Can I put my indoor herb containers outside?
Yes! Move your potted herbs to the patio or deck when the weather warms in the spring and for a boost of sunshine.
How do I know when my herbs need larger containers?
When roots begin to emerge through the drainage holes of its container, it is time to repot the herbs. Replace the potting mix; the organic material in the potting mix breaks down over time. Remove any plants with woody or thickened stems and replace them with new seeds or seedlings.
Do herbs need fertilizer?
The short answer is yes. However, not all herbs have the same fertilizer needs. Herbs roughly fall into two groups. 1. Slow-growing herbs with small leaves or needles and fibrous, woody stems that are native to the mediterranean where they grow culinary lavender, month, marjoram, oregano, rosemary, sage, savory, tarragon and thyme. 2. Fast-growing herbs with larger, thinner leaves. These can be annuals such as basil, borage, cilantro, chervil and dill; bi-annual herbs such as parsley or perennials such as chives. Herbs in the first group generally need less fertilizer than herbs in the second group.
What type of nutrients do herbs need?
Start out by planting herbs in healthy soil rich in organic matter. In addition, they will benefit from an organic complete, slow-release fertilizer containing equal amounts of macronutrients nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. A slow-release fertilizer is especially important if your garden has sandy soil because nutrients wash out quickly. To give fast-growing herbs that you harvest often an extra boost, you can also apply fish emulsion, an organic fertilizer that is high in nitrogen, with an NPK ratio of 4-1-1 or 5-1-1.
How often should I fertilize my herbs?
The frequency of fertilization follows the growth pattern of the herbs. In soil of average fertility, it is usually sufficient to apply a balanced fertilizer in the spring when they break dormancy, or when the new growing season starts. For other herbs, a light monthly application of a slow-release complete fertilizer should be enough – unless the leaves start to look yellow, which may be a sign of nitrogen deficiency. In that case, applying fish emulsion is a quick fix but before you reach for the fertilizer bottle, rule out that the yellowing of leaves is not caused by something else.
How do I fertilize my herbs in a container?
Herbs grown in containers need fertilizer applications more often, because with frequent watering that container plants require, the fertilizer in the potting mix washes out more quickly. Just as with sandy soil, it is important to use slow-release fertilizer. The roots of container plants are in a confined space, unlike herbs grown in the garden or raised beds, which can lead to over fertilization if you are not careful. Organic fertilizers are recommended over synthetic which often contain a high level of salts that can build up in the container over time. To prevent this, it is best to use half the strength of the fertilizer amount specified on the label for any type of fertilizer.
Is it possible to overfertilize herbs?
Adding too much fertilizer to herbs usually leads to an excess of nitrogen, which has undesirable results especially for slow-growing herbs. For basil and other thin-leaved herbs, the fast leaf growth induced by nitrogen is fine because you want your plants to be lush. For rosemary and other Mediterranean herbs however, rapid growth means that there is less concentration of essential oils causing the herbs to become less aromatic and have weaker flavor.
How do I prepare garden soil before planting an herb garden?
Once you have picked the location for growing your herb garden, you will need to prepare the soil. If the soil is sandy or clay heavy, add plenty of compost. Even if your soil is in pretty good condition, working some compost into the soil will help provide nutrients to the herbs while they are growing.
Can I harvest my herbs too often?
Many times, when a new gardener is starting an herb garden, they are afraid that harvesting the herbs frequently will hurt them. The opposite is true. Frequent harvesting of herbs will result in the herb plant producing more and more foliage, which increases the amount you are able to harvest. At the end of the season, you can dry or freeze your herb harvest to enjoy home grown herbs all year long.
I don’t have a good sunny spot outdoors for my herb garden, what can I do?
If your yard is mostly shaded, there is not much you can do to change that, but you can pick shade friendly herbs. Parsley, sweet woodruff and mint are good examples of herbs that don’t require as much light. If you are growing plants in low light, manage your expectations. Your herbs will grow but will be slow and results less impressive.
My container soil is staying wet, what do I do?
Choose a container that allow for water to drain. If you over water or if it rains too much a good pot will allow the water to flow to the bottom without soaking and rotting the roots of your plants. You can use rocks or pottery shards to fill the bottom of the container to help with drainage. This applies outdoors too. If your herbs constantly have wet feet, they won’t thrive. Either plan when planting your garden and add some sand for drainage or pick plants that don’t mind wet roots as much.
My herbs plants are going to seed, why?
The short answer is you are not pruning enough. To prevent rapid growth and encourage a bushy habit, be sure to prune your herb plants regularly. The more you pick off your stems and leaves the longer your herb plant will remain in its production cycle. If you start to see flower heads, snip them right away. When you fail to cut back the plant, it is likely to go to seed and complete its lifecycle. Once that happens, many plants die back. Keep cutting and pinching back flowers to prevent this from happening.
Should I throw away my seeds on their expiration date?
Seeds do not have an expiration date, rather they are a sell by date just like food. The dates on seed packages are guidelines to help you know when your seeds are getting old, but it does not mean you need to toss them. Every plant is different. Some seeds last longer than others. Most seeds, if kept cool and dry, will last 2 – 3 years. If you are unsure test them out by growing microgreens.
Planting Directions
TEMPERATURE
60F
AVERAGE GERM TIME
14 - 21 days
LIGHT REQUIRED
Yes
DEPTH
1/4 inch
SOWING RATE
5 - 6 seeds per inch
MOISTURE
Keep moist until germination
PLANT SPACING
Rows 18 inches a part; thin seedlings 6 inches









Cinnamon Basil (Ocimum Basilicum Cinnamon) - Easy to grow from Basil seeds, Cinnamon Basil makes a great addition to the herb garden or grow it in a container and enjoy the beauty of this attractive herb plant. This Basil herb plant grows 12 to 16 inches high and 12 to 18 inches wide. The sturdy stems are dark purple red, with dark green, cinnamon scented leaves growing up to 2 inches long.
Cinnamon Basil has distinctive cinnamon-colored stems, purple flowers tinged with bronze, and small to medium-sized, dark green leaves. Cinnamon Basil has a strong cinnamon scent. Basil culinary herb is at its most flavorful when fresh. The best time to harvest is just as the plant starts to set flower buds, well before flowers bloom. For harvesting, cut stems just before flowers open, strip leaves and use fresh, or dry on tray in dark, airy place. Leaves may be frozen. Basil herb uses include tomato dishes, pasta sauces, vegetables and soups. You can also use basil in the garden as a companion plant to repel aphids, mites, and tomato hornworms.
How To Grow Basil From Seed: Sow Basil seeds in the garden after all danger of frost has passed. For areas with short growing seasons, start the herb seeds indoors 4 - 8 weeks before setting out. Grow the Cinnamon Basil plant in a rich, well-drained, soil and in full sun. Pinch the tip from the center shoot of Basil after it has grown for 6 weeks to force side growth and prevent early flowering. If flower stalks develop, simply snip them off.
Approximate Seeds Per Ounce: 20,000
Common Questions
Which herbs can thrive in the kitchen?
Not all herbs are suitable for indoor growth. Herbs with woody, bushy growth, like rosemary are too large for indoor herb gardens. Consider other more suitable herbs for an indoor kitchen garden, such as chives, oregano, thyme, dill, mint, basil, cilantro, sage and savory. Each herb has specific growing needs, so ensure to provide the right amount of light, humidity, and air circulation. If using a single large container, ensure that all plants require similar amounts of sunlight and water. For instance, chives and cilantro may not need as much sunlight as dill and oregano.
What are good companion plants for herb gardens?
Pairing herbs based on watering requirements, like planting lavender with thyme or basil with chives, is ideal for maintaining the health of both plants. Avoid companion planting with catnip, lemon balm and mint as they should be grown in separate pots due to their rapid spreading nature that can overtake other plants in your indoor herb garden.
When do I establish an indoor herb garden?
Create a kitchen herb garden by propagating cuttings from your outdoor plants as the weather cools in the fall. If you opt to sow your indoor herb garden from purchased seeds, begin a few weeks before the anticipated first frost of the season. Most herbs can be harvested within a few weeks, so there is no need to plant too far in advance.
Do kitchen herbs need full sun?
Most herbs need 6 hours of sunlight a day to thrive. If you do not have this type of light available in your kitchen, consider a grow light that will run 14-16 hours per day 6 to 12 inches above your plants. NOTE: Rotate herbs periodically when grown in windows to let each part of the plant receive sunlight.
What time of year should you plant herbs?
Herbs grown in indoor gardens can be planted any time of year. Many gardeners prefer to grow their herbs outdoors during the summer growing season, and then move them to their indoor garden before the first frost of fall. If you prefer to start your seeds outdoors, you will need to wait until after danger of frost in the spring or start your seeds indoors 6 -8 weeks before last frost and transplant in your garden after danger of frost.
Do herbs come back every year?
Perennial herbs will come back each year when planted in the correct zone or grown indoors during the cold winter months. Popular perennial herbs are oregano, parsley, sage, fennel, chives, lavender, thyme and mint varieties.
How do I know when my herbs need watered?
Allow the soil to dry out just slightly before watering your herbs again. Give your indoor herb garden a dose of diluted water-soluble fertilizer every 2 weeks or so. Too much food will compromise the taste of the herbs. It is also beneficial to provide adequate humidity. If the indoor air is especially dry – which is often the case in regions with cold winters. Set the herbs pots on trays of stones. Fill the trays with water but keep the level below the drainage holes of your pots.
When do I water my outdoor herb garden?
Different herb plants will need different amounts of water so keep this in mind when planting your garden and keep similar plants together to simplify watering. Watering is best done in the early morning hours when temperatures are cooler. Many herbs are hardy. They can tolerate soil that is moderately dry. You want to keep an eye out for wilting when the soil is wet. Ideally, your herbs should make quick use of the water you give them. Saturated soil is not what you are after. Pay close attention to the coloration of the leaves on your herbs. Yellow leaves can be a sign of too much water, and so can black leaves. If you spot any mildew or fuzz on the herbs, too much moisture can be the problem.
How do I harvest my herbs?
Trim back flowering sections before they bloom for healthier leaves. Prune new growth on young plants weekly to encourage a fuller mature plant. Snip herbs for harvest when they are just a few inches tall. Pruning back the herbs often means a larger, longer harvest. Cut the new growth back at least one per week, even if you are not using the herbs in recipes (see drying and freezing page if you do not want to waste your harvest). Long stems that are about to set flower buds should be trimmed off as they appear.
What do I need to start an indoor herb garden?
Common tools needed for an indoor herb garden are: garden trowel, scissors for snipping, stones (optional). Materials for your herbs plants include seed, pots, potting soil, cactus potting soil (optional), pots or trays, fertilizer and a grow light if you do not have adequate sunlight of at least 6 hours per day for your plants.
How do I prepare my containers for planting?
Choose large, deep containers with drainage holes to accommodate fast-growing herbs. Fill the container with potting mix leaving about ½ inch clear at the top. Use standard commercial potting soil for most herbs but blend in cactus potting mix for herbs native to the Mediterranean, such as thyme and oregano which prefer dryer soils.
Can I put my indoor herb containers outside?
Yes! Move your potted herbs to the patio or deck when the weather warms in the spring and for a boost of sunshine.
How do I know when my herbs need larger containers?
When roots begin to emerge through the drainage holes of its container, it is time to repot the herbs. Replace the potting mix; the organic material in the potting mix breaks down over time. Remove any plants with woody or thickened stems and replace them with new seeds or seedlings.
Do herbs need fertilizer?
The short answer is yes. However, not all herbs have the same fertilizer needs. Herbs roughly fall into two groups. 1. Slow-growing herbs with small leaves or needles and fibrous, woody stems that are native to the mediterranean where they grow culinary lavender, month, marjoram, oregano, rosemary, sage, savory, tarragon and thyme. 2. Fast-growing herbs with larger, thinner leaves. These can be annuals such as basil, borage, cilantro, chervil and dill; bi-annual herbs such as parsley or perennials such as chives. Herbs in the first group generally need less fertilizer than herbs in the second group.
What type of nutrients do herbs need?
Start out by planting herbs in healthy soil rich in organic matter. In addition, they will benefit from an organic complete, slow-release fertilizer containing equal amounts of macronutrients nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. A slow-release fertilizer is especially important if your garden has sandy soil because nutrients wash out quickly. To give fast-growing herbs that you harvest often an extra boost, you can also apply fish emulsion, an organic fertilizer that is high in nitrogen, with an NPK ratio of 4-1-1 or 5-1-1.
How often should I fertilize my herbs?
The frequency of fertilization follows the growth pattern of the herbs. In soil of average fertility, it is usually sufficient to apply a balanced fertilizer in the spring when they break dormancy, or when the new growing season starts. For other herbs, a light monthly application of a slow-release complete fertilizer should be enough – unless the leaves start to look yellow, which may be a sign of nitrogen deficiency. In that case, applying fish emulsion is a quick fix but before you reach for the fertilizer bottle, rule out that the yellowing of leaves is not caused by something else.
How do I fertilize my herbs in a container?
Herbs grown in containers need fertilizer applications more often, because with frequent watering that container plants require, the fertilizer in the potting mix washes out more quickly. Just as with sandy soil, it is important to use slow-release fertilizer. The roots of container plants are in a confined space, unlike herbs grown in the garden or raised beds, which can lead to over fertilization if you are not careful. Organic fertilizers are recommended over synthetic which often contain a high level of salts that can build up in the container over time. To prevent this, it is best to use half the strength of the fertilizer amount specified on the label for any type of fertilizer.
Is it possible to overfertilize herbs?
Adding too much fertilizer to herbs usually leads to an excess of nitrogen, which has undesirable results especially for slow-growing herbs. For basil and other thin-leaved herbs, the fast leaf growth induced by nitrogen is fine because you want your plants to be lush. For rosemary and other Mediterranean herbs however, rapid growth means that there is less concentration of essential oils causing the herbs to become less aromatic and have weaker flavor.
How do I prepare garden soil before planting an herb garden?
Once you have picked the location for growing your herb garden, you will need to prepare the soil. If the soil is sandy or clay heavy, add plenty of compost. Even if your soil is in pretty good condition, working some compost into the soil will help provide nutrients to the herbs while they are growing.
Can I harvest my herbs too often?
Many times, when a new gardener is starting an herb garden, they are afraid that harvesting the herbs frequently will hurt them. The opposite is true. Frequent harvesting of herbs will result in the herb plant producing more and more foliage, which increases the amount you are able to harvest. At the end of the season, you can dry or freeze your herb harvest to enjoy home grown herbs all year long.
I don’t have a good sunny spot outdoors for my herb garden, what can I do?
If your yard is mostly shaded, there is not much you can do to change that, but you can pick shade friendly herbs. Parsley, sweet woodruff and mint are good examples of herbs that don’t require as much light. If you are growing plants in low light, manage your expectations. Your herbs will grow but will be slow and results less impressive.
My container soil is staying wet, what do I do?
Choose a container that allow for water to drain. If you over water or if it rains too much a good pot will allow the water to flow to the bottom without soaking and rotting the roots of your plants. You can use rocks or pottery shards to fill the bottom of the container to help with drainage. This applies outdoors too. If your herbs constantly have wet feet, they won’t thrive. Either plan when planting your garden and add some sand for drainage or pick plants that don’t mind wet roots as much.
My herbs plants are going to seed, why?
The short answer is you are not pruning enough. To prevent rapid growth and encourage a bushy habit, be sure to prune your herb plants regularly. The more you pick off your stems and leaves the longer your herb plant will remain in its production cycle. If you start to see flower heads, snip them right away. When you fail to cut back the plant, it is likely to go to seed and complete its lifecycle. Once that happens, many plants die back. Keep cutting and pinching back flowers to prevent this from happening.
Should I throw away my seeds on their expiration date?
Seeds do not have an expiration date, rather they are a sell by date just like food. The dates on seed packages are guidelines to help you know when your seeds are getting old, but it does not mean you need to toss them. Every plant is different. Some seeds last longer than others. Most seeds, if kept cool and dry, will last 2 – 3 years. If you are unsure test them out by growing microgreens.
Planting Directions
TEMPERATURE
70F
AVERAGE GERM TIME
7 - 14 days
LIGHT REQUIRED
Yes
DEPTH
1/4 inch
SOWING RATE
5 - 6 seeds per inch
MOISTURE
Keep seeds moist until germination
PLANT SPACING
Rows 18 inches a part; thin seedlings 6 inches








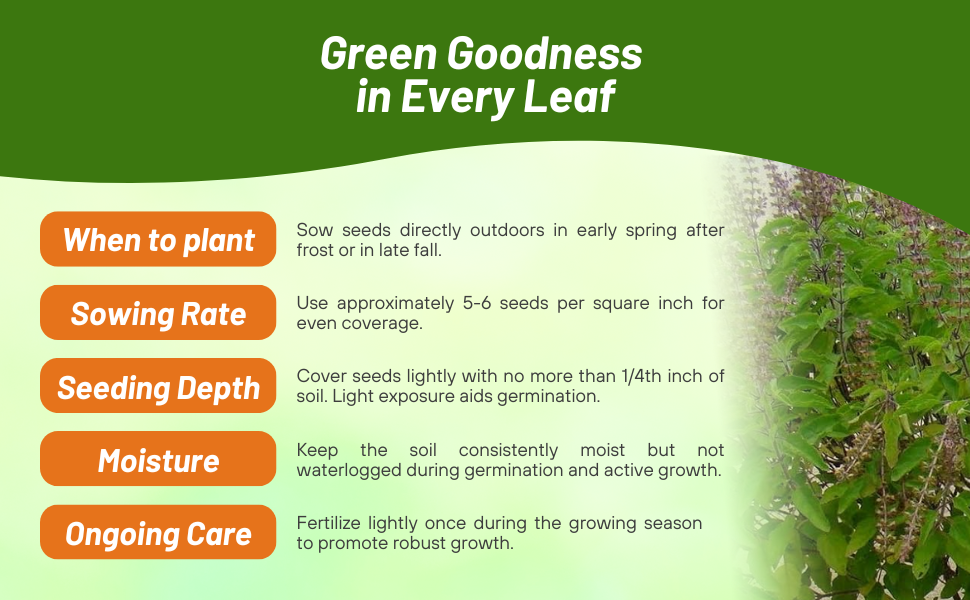
Green Holy Basil (Ocimum Sanctum) - Holy Basil is a widely cultivated herb plant that can be grown from Basil seeds. It is a tender perennial, and in many areas is grown as an annual. Holy Basil is a bushy, aromatic herb that is native to Asia but now is grown in many warm climates world-wide. It has a pungent, peppery flavor and can be used as a culinary herb. There are two main types of Holy Basil: green-leaved and purple-leaved.
Holy Basil plants are extremely important in the Hindu religion. In the Hindu religion the herb plants, called Tulsi, are worshiped morning and evening. As a medicinal herb, Tulsi Holy Basil is used to fight fevers associated with malaria, dengue fever, colds and flu by making a tea from the leaves. The Holy Basil teas also soothe sore throats, coughs, and respiratory ailments. Holy Basil is considered to be an adaptogen and helps protect the body against stress.
How To Grow Holy Basil From Herb Seeds: Start the Holy Basil herb seeds indoors 6 - 8 weeks before the end of frost season. Use a good, sterilized seed starting mix. Keep the soil moist but not saturated until germination occurs. In warm climates, the Basil seeds can be directly started outdoors in prepared seedbeds. The Holy Basil plants benefit from regular fertilizer feeding. Start feeding once the first true leaves appear, and used a diluted liquid fertilizer, like fish emulsion, every other week.
Common Questions
Which herbs can thrive in the kitchen?
Not all herbs are suitable for indoor growth. Herbs with woody, bushy growth, like rosemary are too large for indoor herb gardens. Consider other more suitable herbs for an indoor kitchen garden, such as chives, oregano, thyme, dill, mint, basil, cilantro, sage and savory. Each herb has specific growing needs, so ensure to provide the right amount of light, humidity, and air circulation. If using a single large container, ensure that all plants require similar amounts of sunlight and water. For instance, chives and cilantro may not need as much sunlight as dill and oregano.
What are good companion plants for herb gardens?
Pairing herbs based on watering requirements, like planting lavender with thyme or basil with chives, is ideal for maintaining the health of both plants. Avoid companion planting with catnip, lemon balm and mint as they should be grown in separate pots due to their rapid spreading nature that can overtake other plants in your indoor herb garden.
When do I establish an indoor herb garden?
Create a kitchen herb garden by propagating cuttings from your outdoor plants as the weather cools in the fall. If you opt to sow your indoor herb garden from purchased seeds, begin a few weeks before the anticipated first frost of the season. Most herbs can be harvested within a few weeks, so there is no need to plant too far in advance.
Do kitchen herbs need full sun?
Most herbs need 6 hours of sunlight a day to thrive. If you do not have this type of light available in your kitchen, consider a grow light that will run 14-16 hours per day 6 to 12 inches above your plants. NOTE: Rotate herbs periodically when grown in windows to let each part of the plant receive sunlight.
What time of year should you plant herbs?
Herbs grown in indoor gardens can be planted any time of year. Many gardeners prefer to grow their herbs outdoors during the summer growing season, and then move them to their indoor garden before the first frost of fall. If you prefer to start your seeds outdoors, you will need to wait until after danger of frost in the spring or start your seeds indoors 6 -8 weeks before last frost and transplant in your garden after danger of frost.
Do herbs come back every year?
Perennial herbs will come back each year when planted in the correct zone or grown indoors during the cold winter months. Popular perennial herbs are oregano, parsley, sage, fennel, chives, lavender, thyme and mint varieties.
How do I know when my herbs need watered?
Allow the soil to dry out just slightly before watering your herbs again. Give your indoor herb garden a dose of diluted water-soluble fertilizer every 2 weeks or so. Too much food will compromise the taste of the herbs. It is also beneficial to provide adequate humidity. If the indoor air is especially dry – which is often the case in regions with cold winters. Set the herbs pots on trays of stones. Fill the trays with water but keep the level below the drainage holes of your pots.
When do I water my outdoor herb garden?
Different herb plants will need different amounts of water so keep this in mind when planting your garden and keep similar plants together to simplify watering. Watering is best done in the early morning hours when temperatures are cooler. Many herbs are hardy. They can tolerate soil that is moderately dry. You want to keep an eye out for wilting when the soil is wet. Ideally, your herbs should make quick use of the water you give them. Saturated soil is not what you are after. Pay close attention to the coloration of the leaves on your herbs. Yellow leaves can be a sign of too much water, and so can black leaves. If you spot any mildew or fuzz on the herbs, too much moisture can be the problem.
How do I harvest my herbs?
Trim back flowering sections before they bloom for healthier leaves. Prune new growth on young plants weekly to encourage a fuller mature plant. Snip herbs for harvest when they are just a few inches tall. Pruning back the herbs often means a larger, longer harvest. Cut the new growth back at least one per week, even if you are not using the herbs in recipes (see drying and freezing page if you do not want to waste your harvest). Long stems that are about to set flower buds should be trimmed off as they appear.
What do I need to start an indoor herb garden?
Common tools needed for an indoor herb garden are: garden trowel, scissors for snipping, stones (optional). Materials for your herbs plants include seed, pots, potting soil, cactus potting soil (optional), pots or trays, fertilizer and a grow light if you do not have adequate sunlight of at least 6 hours per day for your plants.
How do I prepare my containers for planting?
Choose large, deep containers with drainage holes to accommodate fast-growing herbs. Fill the container with potting mix leaving about ½ inch clear at the top. Use standard commercial potting soil for most herbs but blend in cactus potting mix for herbs native to the Mediterranean, such as thyme and oregano which prefer dryer soils.
Can I put my indoor herb containers outside?
Yes! Move your potted herbs to the patio or deck when the weather warms in the spring and for a boost of sunshine.
How do I know when my herbs need larger containers?
When roots begin to emerge through the drainage holes of its container, it is time to repot the herbs. Replace the potting mix; the organic material in the potting mix breaks down over time. Remove any plants with woody or thickened stems and replace them with new seeds or seedlings.
Do herbs need fertilizer?
The short answer is yes. However, not all herbs have the same fertilizer needs. Herbs roughly fall into two groups. 1. Slow-growing herbs with small leaves or needles and fibrous, woody stems that are native to the mediterranean where they grow culinary lavender, month, marjoram, oregano, rosemary, sage, savory, tarragon and thyme. 2. Fast-growing herbs with larger, thinner leaves. These can be annuals such as basil, borage, cilantro, chervil and dill; bi-annual herbs such as parsley or perennials such as chives. Herbs in the first group generally need less fertilizer than herbs in the second group.
What type of nutrients do herbs need?
Start out by planting herbs in healthy soil rich in organic matter. In addition, they will benefit from an organic complete, slow-release fertilizer containing equal amounts of macronutrients nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. A slow-release fertilizer is especially important if your garden has sandy soil because nutrients wash out quickly. To give fast-growing herbs that you harvest often an extra boost, you can also apply fish emulsion, an organic fertilizer that is high in nitrogen, with an NPK ratio of 4-1-1 or 5-1-1.
How often should I fertilize my herbs?
The frequency of fertilization follows the growth pattern of the herbs. In soil of average fertility, it is usually sufficient to apply a balanced fertilizer in the spring when they break dormancy, or when the new growing season starts. For other herbs, a light monthly application of a slow-release complete fertilizer should be enough – unless the leaves start to look yellow, which may be a sign of nitrogen deficiency. In that case, applying fish emulsion is a quick fix but before you reach for the fertilizer bottle, rule out that the yellowing of leaves is not caused by something else.
How do I fertilize my herbs in a container?
Herbs grown in containers need fertilizer applications more often, because with frequent watering that container plants require, the fertilizer in the potting mix washes out more quickly. Just as with sandy soil, it is important to use slow-release fertilizer. The roots of container plants are in a confined space, unlike herbs grown in the garden or raised beds, which can lead to over fertilization if you are not careful. Organic fertilizers are recommended over synthetic which often contain a high level of salts that can build up in the container over time. To prevent this, it is best to use half the strength of the fertilizer amount specified on the label for any type of fertilizer.
Is it possible to overfertilize herbs?
Adding too much fertilizer to herbs usually leads to an excess of nitrogen, which has undesirable results especially for slow-growing herbs. For basil and other thin-leaved herbs, the fast leaf growth induced by nitrogen is fine because you want your plants to be lush. For rosemary and other Mediterranean herbs however, rapid growth means that there is less concentration of essential oils causing the herbs to become less aromatic and have weaker flavor.
How do I prepare garden soil before planting an herb garden?
Once you have picked the location for growing your herb garden, you will need to prepare the soil. If the soil is sandy or clay heavy, add plenty of compost. Even if your soil is in pretty good condition, working some compost into the soil will help provide nutrients to the herbs while they are growing.
Can I harvest my herbs too often?
Many times, when a new gardener is starting an herb garden, they are afraid that harvesting the herbs frequently will hurt them. The opposite is true. Frequent harvesting of herbs will result in the herb plant producing more and more foliage, which increases the amount you are able to harvest. At the end of the season, you can dry or freeze your herb harvest to enjoy home grown herbs all year long.
I don’t have a good sunny spot outdoors for my herb garden, what can I do?
If your yard is mostly shaded, there is not much you can do to change that, but you can pick shade friendly herbs. Parsley, sweet woodruff and mint are good examples of herbs that don’t require as much light. If you are growing plants in low light, manage your expectations. Your herbs will grow but will be slow and results less impressive.
My container soil is staying wet, what do I do?
Choose a container that allow for water to drain. If you over water or if it rains too much a good pot will allow the water to flow to the bottom without soaking and rotting the roots of your plants. You can use rocks or pottery shards to fill the bottom of the container to help with drainage. This applies outdoors too. If your herbs constantly have wet feet, they won’t thrive. Either plan when planting your garden and add some sand for drainage or pick plants that don’t mind wet roots as much.
My herbs plants are going to seed, why?
The short answer is you are not pruning enough. To prevent rapid growth and encourage a bushy habit, be sure to prune your herb plants regularly. The more you pick off your stems and leaves the longer your herb plant will remain in its production cycle. If you start to see flower heads, snip them right away. When you fail to cut back the plant, it is likely to go to seed and complete its lifecycle. Once that happens, many plants die back. Keep cutting and pinching back flowers to prevent this from happening.
Should I throw away my seeds on their expiration date?
Seeds do not have an expiration date, rather they are a sell by date just like food. The dates on seed packages are guidelines to help you know when your seeds are getting old, but it does not mean you need to toss them. Every plant is different. Some seeds last longer than others. Most seeds, if kept cool and dry, will last 2 – 3 years. If you are unsure test them out by growing microgreens.
































